Why in News?
Confined field trials of two Genetically Modified Crops (GM) maize varieties—herbicide-tolerant and insect-resistant—are set to begin at Punjab Agricultural University after approval from the GEAC and Punjab government, sparking opposition from GM-Free India over glyphosate concerns.
Description:
- Genetic Modification is the insertion of a foreign gene (usually with a desired trait) into the DNA of an organism.
- In plants, this is done to introduce traits like pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, disease resistance, or improved nutritional quality.
First Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops):
- Flavr Savr Tomato (USA, 1994): Developed to delay ripening and spoilage.
Most Common Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops) (Worldwide):
- Cotton, Soybean, Maize, Canola
- Traits: Mainly herbicide tolerance and insect resistance.
Top 5 Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops) Growing Countries (≈90% of global area):
- USA
- Brazil
- Argentina
- India
- Canada
Bt Technology:
- Derived from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), a soil bacterium.
- Produces Cry and Cyt toxins which kill insects like caterpillars, beetles, mosquitoes, etc.
- Example: Bt Cotton (insect-resistant to bollworms)
Methods of Genetic Modification:
| Method | Description |
| Agrobacterium tumefaciens | Soil bacterium used as a vector; carries desired gene via Ti-plasmid |
| Gene Gun (Biolistics) | DNA-coated gold or tungsten particles are shot into the plant cell |
| Electroporation | Uses electric pulses to open cell membrane and insert DNA |
| Microinjection | Physical insertion of DNA directly into nucleus using a micropipette |
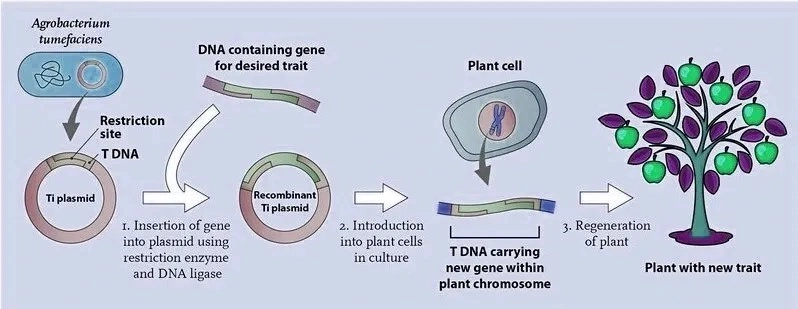
Advantages of Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops):
- Pest Resistance → Reduces pesticide use (e.g., Bt Cotton)
- Virus Resistance → Crops can be modified to resist specific viruses
- Drought Tolerance → Helps conserve groundwater
- Herbicide Tolerance → No need for tilling; prevents soil erosion
- Nutritional Enhancement → e.g., Golden Rice (rich in β-carotene)
- Sustainability → Encourages no-till farming (carbon sequestration)
- Biofortification → Increases micronutrient content in crops
- Edible Vaccines, Phytoremediation, Biofuels (from GM algae)
Disadvantages / Concerns:
- Health Risks → Horizontal gene transfer may spread antibiotic resistance
- Superweeds → Weeds become resistant to herbicides (e.g., glyphosate resistance)
- Pest Resistance → Pests may adapt to Bt toxins
- Genetic Pollution → Cross-breeding may reduce local biodiversity
- Impact on Pollinators → Honeybee populations could be affected
Applications:
- Golden Rice: Biofortified rice with Vitamin A precursor
- Edible Vaccines: Express vaccine proteins in fruits or vegetables
- Phytoremediation: GM plants that detoxify pollutants
- 4th Gen Biofuels: From GM algae and cyanobacteria
Regulatory Framework in India:
| Body | Function |
| RDAC (Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee) | Monitors biotech developments nationally & globally |
| RCGM (Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation) | Oversees research and field trials; reviews safety |
| GEAC (Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee) | Approves environmental release; under MoEFCC |
| SBCC (State Biotechnology Coordination Committee) | Implements and monitors GM safety measures at the state level |
Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops) in India – Status:
| GM Crop | Status |
| Bt Cotton | Commercialised in 2002 (only GM crop approved for cultivation) |
| Bt Brinjal | Approved in 2009, but under moratorium since 2010 |
| GM Mustard | Field trials allowed, but commercial cultivation not started |
| GM Maize, Chickpea, Tomato | Under various stages of field trials |
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
