Paper: GS – III, Subject: Economy, Topic: Trade and External Sector, Issue: Implications of rising tariffs.
Context:
The world is witnessing a reversal of globalization, marked by rising tariffs, protectionism, and anti-global sentiment.This phenomenon in the broader context of political, economic, and technological developments from the late 20th century to the present.
Key Highlights:
Globalization: Refers to the shrinking of distances, cross-border movement of goods, people, and ideas, and international cooperation. It is historically driven by innovations like the telegraph, railroads, and steamships in the 19th century.
Waves of Globalization:
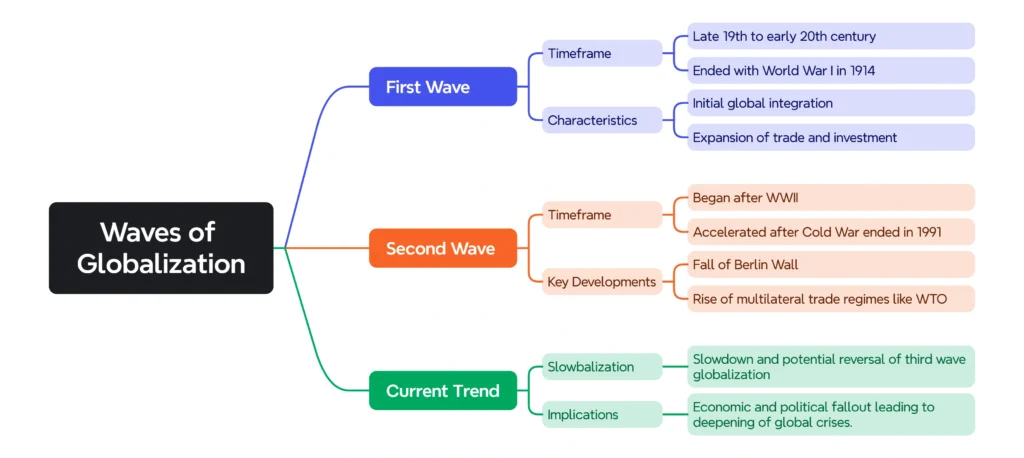
Factors Contributing to De-globalization:
- Tariff Wars and Protectionism: US trade wars, especially under the Trump administration, increased tariffs and restricted global trade.UK Prime Minister’s office (2024) has already declared that “globalization is over.”
- Anti-Global Political Movements: Anti-WTO protests (Seattle, 1999) reflected early signs of backlash with the rise of populist, anti-immigrant politics in US and Europe.
- Global Financial Crisis (2008): Shook the trust in globalization and questioned the justice and stability of global capitalism which benefited populist parties.
- Covid-19 Pandemic: Exposed overdependence on global supply chains, especially for essentials and prompted reshoring and national self-reliance measures.
- Refugee Crises: as seen in the European refugee backlash post-2015. Brexit and Trump-era policies are also linked to anti-immigrant sentiment.
Slowbalization:
Coined by The Economist, it refers to slowing pace of globalization, not complete reversal. It is characterized by:
- Low global trade growth
- Barriers to migration
- Rise of digital sovereignty and nationalism
Impacts of Slowbalization:
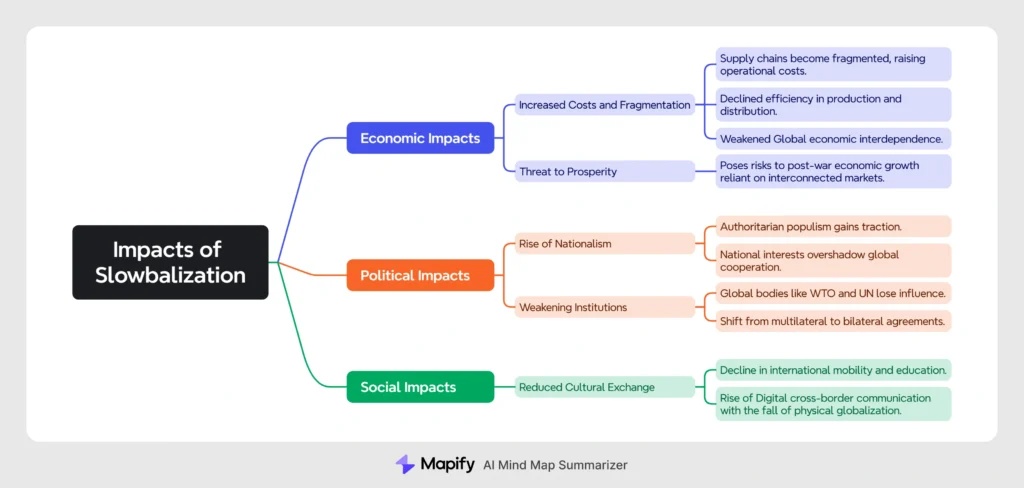
Historical Parallels: Austrian writer Stefan Zweig noted that pre-WWI global integration was assumed permanent but collapsed in 1914.Similar overconfidence in irreversible globalization exists today.
Way Forward:
- Recalibrate globalization to be more inclusive, equitable, and resilient.
- Strengthen global institutions and multilateral norms.
- Promote sustainable interdependence not isolationism.
- Embrace technological globalization (digital economy), while balancing geopolitical tensions.
- India must:
- Navigate global protectionist trends wisely.
- Use opportunities in digital trade and services.
- Reduce overdependence on global supply chains while staying export-competitive.
- Engage actively in global forums (e.g., WTO, G20) to protect interests of the Global South.
Conclusion:
While the world is not witnessing the end of globalization, it is undergoing a fundamental transformation. This “slowbalization” demands nuanced, adaptive, and evidence-based policy responses, especially for emerging economies like India.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
