Paper: GS – III, Subject: Science and Technology, Topic: Nuclear Technology, Issue: Data Centres & AI Energy Demand.
Context:
The Indian government is considering encouraging the use of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) to power the rapidly growing data centre sector, especially driven by artificial intelligence (AI) demands.
Key Takeaways:
The Rationale: Powering the AI Revolution:
- Exponential Growth of Data Centers: The rise of AI is causing data centers to grow exponentially, leading to a massive surge in energy demand.
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that data center power usage could double by 2026.
- Sustainability Concerns: The increasing energy consumption of data centers poses a challenge to companies aiming for net-zero or carbon-negative goals by 2030.
- Major players like Google and Microsoft are already signing deals with nuclear power plants to secure clean energy for their data centers.
- Economic Significance: Power consumption and related infrastructure constitute a significant portion of data center expenditure.
- Electrical systems account for 40% of capital expenditure, and electricity consumption represents 65% of operating costs.
- Setting up one MW of data center capacity in India costs between Rs 60-70 crore.
- Market Growth: India’s data center market is estimated to be worth $10 billion, with revenue of around $1.2 billion in FY24.
- The country is expected to add 795 MW of new capacity by 2027, reaching a total capacity of 1.8 GW.
- Limitations of Renewables: While renewable energy sources are preferred, they face limitations such as intermittency (dependence on sunlight and wind) and lack of adequate storage options.
- Nuclear as a Solution: Nuclear energy offers a clean, round-the-clock power source that can overcome the limitations of renewables, providing a reliable energy supply for AI applications and data centers.
About the Small Modular Reactors (SMRs):
- These are a type of nuclear reactor designed to be smaller in size and capacity compared to traditional nuclear reactors.
- Typically, SMRs have a capacity of up to 300 megawatts (MW), which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors.
- Small physically a fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor.
- Modular – making it possible for systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation.
- Reactors – harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
Global Examples:
- Akademik Lomonosov (Russia): A floating power unit with two 35 MWe modules, operational since May 2020.
- HTR-PM (China): A demonstration SMR project connected to the grid in December 2021, reportedly commercially operational since December 2023.
- India’s Ambitions: India aims to enter the manufacturing value chain of SMRs, both to fulfill its clean energy commitments and to promote SMRs as a technology-led foreign policy initiative.
Data Centres Using Nuclear Power:
- Google (United States): Google has signed long-term agreements with nuclear power plants to supply clean energy for its data centres, aiming to achieve carbon-free operations 24/7.
- Microsoft (United States): Microsoft is also collaborating with nuclear power providers, including companies developing SMRs, to ensure a stable and clean energy supply for its expanding data centre infrastructure focused on AI.
Policy Changes Under Consideration:
To facilitate the adoption of nuclear energy for data centers, the Indian government is considering two major policy changes:
- Easing Nuclear Liability Laws: The Issue: The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010, intended to compensate victims of nuclear accidents, has been cited as an impediment by foreign equipment vendors like Westinghouse Electric and Framatome.
- The Concern: The legislation channels operator liability to suppliers through a “right of recourse” provision.
- The Solution: The government is considering easing provisions in the act to address these concerns.
Enabling Private Sector Participation:
- The Goal: To allow private companies to participate in nuclear power plant operations in India.
- The Potential: This could pave the way for foreign companies to take minority equity stakes in upcoming nuclear power projects.
Challenges and Measures for SMRs in India:
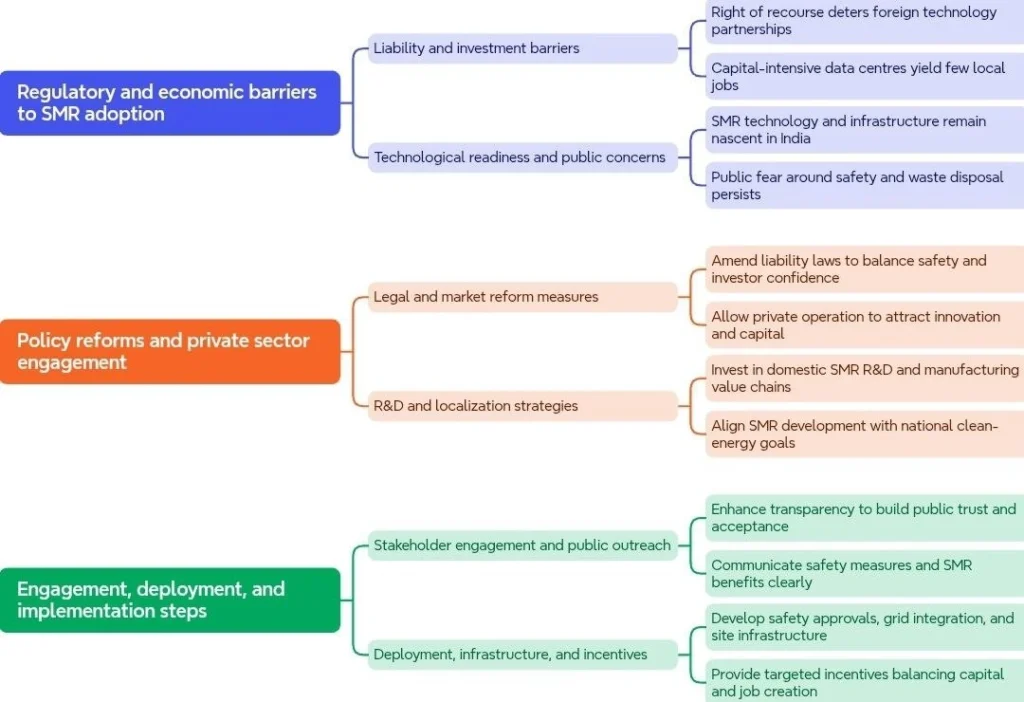
SMR-led nuclear power can provide India’s data centres with clean, reliable energy to meet rising 24/7 demand. Despite challenges like regulation, costs, and public acceptance, policy reforms, private investment, and technology development could make India a leader in SMRs. This would support digital growth while advancing the country’s low-carbon transition.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
