Paper: GS – III, Subject: Indian Economy, Topic: Economy related schemes and Policies, Issue: India’s Mineral Mission.
Context:
The Union Cabinet’s rare-earth magnet scheme and the G-20 framework on critical minerals highlight the importance of value creation through refining and manufacturing.
Key Highlights:
India’s mining law reforms have improved digging capabilities, but the country still lacks large-scale processing facilities.
Vulnerability and Exposure:
- India imports almost all of its lithium, nickel, and cobalt, which are essential for clean energy technologies.
- However, the stakes extend beyond clean energy, as high-purity materials are also crucial for semiconductors, telecommunications, automobiles, pharmaceuticals, and defense systems.
- The midstream segment of the critical minerals value chain (processing and refining) is a global chokepoint, with China controlling over 90% of global rare earths and graphite refining.
- China’s tightening of export controls on rare earth and battery technologies further exposes India’s vulnerability.
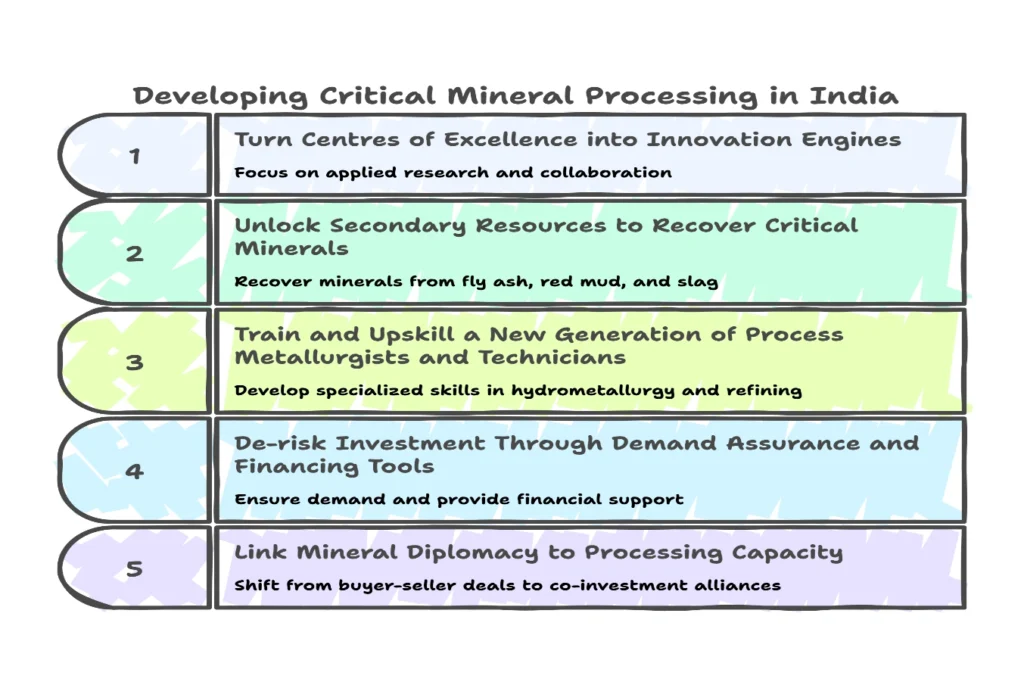
Train and Upskill a New Generation of Process Metallurgists and Technicians:
- Critical minerals require specialized hydrometallurgical and advanced refining techniques.
- The ₹100 crore allocation under the National Critical Mission (NCMM) for skilled workforce development should fund train-the-trainer programs for existing workers, diploma-level courses, and new curricula at academic and CSIR labs.
- Developing such a workforce could create thousands of skilled jobs.
De-risk Investment Through Demand Assurance and Financing Tools:
- The U.S. Department of Defense’s deal with MP Materials, which combines government offtake commitments and price guarantees, offers a model.
- India could adapt this by turning its proposed stockpiling of critical minerals under the Mission into an active market-maker, buying from domestic producers during downturns and releasing during demand surges.
Link Mineral Diplomacy to Processing Capacity:
- India’s recent overseas acquisitions are significant but focus mainly on getting access to raw ores.
- If India can demonstrate consistent high-purity refining across the seven minerals it already handles, it could shift global partnerships from buyer-seller deals to co-investment alliances.
- Critical mineral parks could serve as collaboration hubs where foreign firms co-invest and co-process.
With China tightening mineral and technology exports, India must master the art of turning ores into materials. Processing is the missing link that will determine whether India remains a supplier of raw resources or becomes a builder of resilient and clean industries.
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/a-missing-link-in-indias-mineral-mission/article70353161.ece
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
