Paper: GS – III, Subject: Environment and Ecology, Topic: Global Efforts, Issue: US Exits Key Global Climate Institutions.
Context:
The United States has announced its withdrawal from the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change along with over 60 international treaties and organisations, including the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, International Solar Alliance, and International Renewable Energy Agency.
Key Takeaways:
- This follows the earlier US exit from the Paris Agreement, which becomes effective in January 2026. The decision marks a near-total disengagement of the US from the global climate governance architecture.
| Organization | Established | Goal | Purpose | Headquarters |
| UNFCCC | 1992 (Rio Earth Summit); entered force 1994 | Stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations to prevent dangerous climate interference | Facilitates international negotiations, legal frameworks like Paris Agreement, and COP meetings for mitigation, adaptation, finance | Bonn, Germany |
| IPCC | 1988 (by UNEP and WMO) | Provide policymakers with rigorous climate assessments | Reviews peer-reviewed science on climate impacts, adaptation, mitigation via Assessment Reports; neutral policy advice | Geneva, Switzerland |
| ISA | 2015 (India-France initiative); HQ treaty 2023 | Achieve 1,000 GW solar capacity globally by 2030 | Promotes solar energy in tropical nations through investment, tech transfer, policy support (India-led) | Gurugram, India |
| IRENA | 2009 (founding statute); operational 2012 | Lead global renewable energy transition per Paris Agreement | Offers policy analysis, cost data, capacity building for all renewables (solar, wind, etc.) | Abu Dhabi, UAE |
Background:
- The US was instrumental in shaping the UNFCCC, which established principles such as common but differentiated responsibilities.
- However, it never ratified the Kyoto Protocol (1997), which imposed binding emission targets on developed countries.
- The US later pushed for a more flexible framework, culminating in the Paris Agreement (2015), based on voluntary Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- Despite remaining engaged in climate science and clean technology innovation, the US record on emission reductions, climate finance, and technology transfer has been weak.
- Under President Donald Trump, the US has openly questioned climate science, reduced funding for climate research, and reversed regulatory measures.
Key Highlights of the Decision:
- Formal withdrawal from UNFCCC, IPCC, ISA, and IRENA
- Termination of multilateral engagement on climate mitigation, adaptation, and finance
- Sharp cuts in funding and staffing of US climate research institutions
- Complete exit from rule-making and consensus-building platforms on climate change
Significance of US withdrawal from Climate Cooperation:
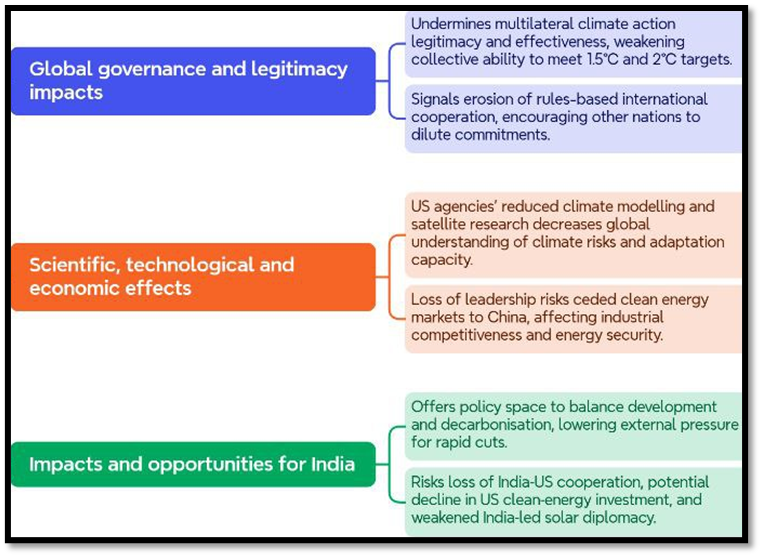
Examples & Data (Value Addition):
- The US has historically failed to meet its emission reduction commitments under the Paris framework
- Renewable energy costs (solar and wind) have declined sharply, making clean energy economically viable
- China controls a significant share of global solar panel and battery manufacturing, positioning itself as a climate-tech leader
Way Forward:
For the Global Community:
- Strengthen climate coalitions excluding reluctant actors
- Enhance South-South cooperation on clean energy
- Insulate climate science from political interference
For India:
- Diversify climate partnerships with EU, Japan, and emerging economies
- Accelerate domestic clean energy manufacturing under Atmanirbhar Bharat
- Leverage leadership roles in ISA and G20 to shape climate discourse
Conclusion:
By vacating the climate space, the US risks undermining not only global climate action but also its own strategic and economic interests. For countries like India, the challenge lies in navigating reduced cooperation while sustaining momentum towards a resilient and sustainable energy transition.
Source: (The Indian Express)
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2026 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
