Paper: GS – II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Agreements involving India, Issue: India–EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
Context:
After almost two decades of negotiations, India and the European Union have concluded a landmark Free Trade Agreement (FTA), described as the “Mother of all Deals,” which is poised to enhance India’s exports and reinforce its vision of Viksit Bharat@2047.
Key Takeaways:
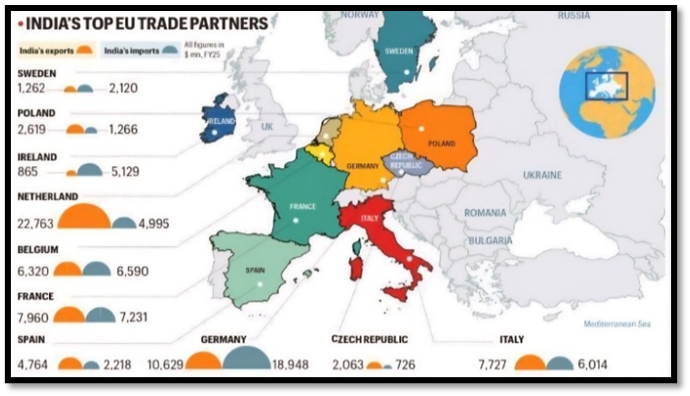
| About European Union: The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 European countries that work together on trade, governance, and regional development. It has a single market allowing free movement of goods, services, people, and capital among member states. Formation and Members: Established in 1993 by the Maastricht Treaty, the EU consists of 27 member states, including Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands. Single Market: Promotes free movement of goods, services, people, and capital across member countries, creating one of the largest economic zones in the world. Common Policies: The EU coordinates on trade, agriculture, competition, environment, energy, and foreign policy to maintain regional stability and growth. Euro Currency: 19 of the 27 member states use the euro as their official currency, facilitating economic integration. Global Economic Influence: The EU is one of the largest trading blocs, contributing around 15-17% of global exports and a major source of FDI worldwide. |
The Trade Deal: The “Big Swap”
The core of the FTA is a strategic trade-off: India gets market access for labor-intensive goods, while the EU gets access for high-value industrial goods.
| What India Gains | What EU Gains | ||
| Area | Details | Area | Details |
| Duty-Free Market Access | 99.5% of Indian exports to the EU will enjoy 0% tariff | Tariff Liberalisation | Tariffs removed or reduced on 97% of EU goods entering India |
| Textiles & Apparel | Tariffs reduced to 0% (earlier up to 12%), placing India at par with Vietnam and Bangladesh | Automobiles | Import duties slashed from 110% to 10% (quota: 250,000 vehicles per year) |
| Leather, Gems & Jewellery, Sports Goods | Zero-duty access to EU markets | Wines & Spirits | Wine duties cut from 150% to 20–30%; spirits duty reduced to 40% |
| Steel | Duty-free quota of 1.6 million tonnes | Aircraft | Zero tariffs on Airbus aircraft exports to India |
| Mobility & Visas | Mobility Pact enabling uncapped student mobility and easier work norms for Indian professionals (IT, nursing, accounting) across 27 EU nations | – | – |
The Negative List (Exclusions): To protect domestic interests, Agriculture (Dairy, beef, chicken, wheat, rice) has been excluded from the deal.
The “CBAM” Hurdle (Carbon Tax):
The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) was a major sticking point. The EU plans to tax carbon-intensive imports (steel, aluminum, cement) starting Jan 1, 2026.
- The Issue: Indian steel/aluminum makers feared a 20-30% tax, acting as a “non-tariff barrier.”
- The Solution: India negotiated a “flexibility” clause similar to the US. India can use its domestic carbon taxes/compliance to offset the EU border tax.
- Recycling: India gained access to EU steel scrap (crucial for low-carbon steel production), which was previously restricted under EU recycling policies.
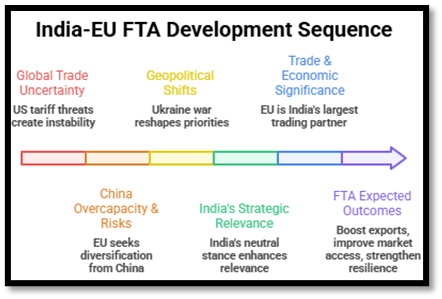
Geopolitical Shift: Ukraine & Security:
The summit marked a significant “subtle shift” in India’s diplomatic stance.
- Ukraine Stance: The joint statement supports the “independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity” of Ukraine. This is a departure from India’s previous neutral language and is seen as a move closer to the EU position, distancing slightly from Russia.
- Security & Defence Partnership (SDP):
- First-ever overarching security pact signed.
- Focus on: Maritime security (Indo-Pacific), Cyber threats, Space, and Counter-terrorism.
Technology & Innovation (Agenda 2030):
The leaders adopted the “India-EU Joint Comprehensive Strategic Agenda 2026-2030.”
- TTC (Trade & Technology Council): Continued focus on AI, semiconductors, and clean tech.
- Innovation Hubs: Setting up joint hubs to support startups and cross-border investments.
- Space: Collaboration on satellite navigation and earth observation.
The India–EU Deal goes beyond trade, emerging as a comprehensive strategic partnership integrating economics, security, technology, and mobility. While regulatory challenges persist, the agreement positions India as a key global economic and geopolitical partner in a rapidly shifting world order.
Source: (The Indian Express, The Hindu)
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2026 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
