On 1st February 2026 (Magha Purnima), Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2026–27 — a Budget that goes far beyond annual expenditure planning. It lays down a medium-to-long term development architecture focused on productivity, strategic autonomy, human capital, fiscal discipline and inclusive regional growth.
Unlike short-term stimulus budgets, this one seeks to institutionalise reforms across manufacturing, infrastructure, agriculture, finance, skilling and governance — making it highly relevant for UPSC GS-2, GS-3 and Essay papers.
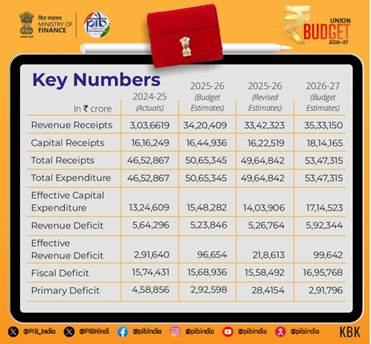
1. Fiscal Framework: Growth with Macroeconomic Stability
The Budget continues India’s calibrated fiscal consolidation while maintaining high development spending.
Key fiscal indicators include:
- Total expenditure of ₹53.5 lakh crore with non-debt receipts of ₹36.5 lakh crore.
- Capital expenditure at ₹12.2 lakh crore — sustaining infrastructure-led growth momentum.
- Fiscal deficit at 4.3 percent of GDP, steadily moving towards long-term prudence.
- Debt-to-GDP ratio at 55.6 percent, with a clear anchor of 50 plus/minus 1 percent by 2030–31.
- Net market borrowings of ₹11.7 lakh crore, enabling investment without destabilising inflation.
- Net tax receipts estimated at ₹28.7 lakh crore.
Federal cooperation is reinforced through the 16th Finance Commission retaining 41 percent vertical devolution and providing ₹1.4 lakh crore in grants to States.
This reflects India’s transition towards rule-based fiscal governance, balancing growth needs with financial sustainability.
2. Three Kartavya Framework: A New Governance Philosophy
The Budget introduces a guiding development ethic built around three national duties.
- Kartavya 1 focuses on accelerating and sustaining economic growth through productivity, competitiveness and resilient supply chains.
- Kartavya 2 aims at fulfilling aspirations and building national capacity by investing in skilling, services leadership and youth employment.
- Kartavya 3 strengthens inclusive development by ensuring equitable access to resources, infrastructure and welfare across regions and communities.
This marks a shift from welfare consumption to capability-based development — a core theme in modern development economics.
#Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27. #Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27
3. Manufacturing Push: Strategic Autonomy and High-Value Industrial Growth
The government has identified seven frontier sectors to deepen industrial capacity and reduce external dependence.
- Biopharma SHAKTI receives ₹10,000 crore over five years, expanding NIPER institutions, upgrading regulatory infrastructure and creating over 1,000 clinical trial sites — positioning India as a global pharmaceutical R&D hub.
- India Semiconductor Mission 2.0 moves beyond assembly to full-stack manufacturing, including indigenous IP, equipment production and industry-led R&D centres.
- Electronics component manufacturing outlay increases to ₹40,000 crore to strengthen domestic supply chains.
- Rare Earth Corridors in Odisha, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu integrate mining, processing and research — critical for EVs, renewables and defence technologies.
- Three chemical parks will follow a cluster-based plug-and-play model to boost scale and compliance.
- Capital goods manufacturing is strengthened through hi-tech tool rooms, infrastructure equipment schemes and a ₹10,000 crore container manufacturing programme.
- The textile sector receives an integrated five-part reform package covering fibre development, employment expansion, handloom and handicraft revival, eco-textiles and Samarth 2.0 along with mega textile parks.
Together, these reforms aim to move India from low-value assembly to innovation-led manufacturing sovereignty.
#Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27. #Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27
4. Infrastructure, Logistics and Energy Transition
Infrastructure remains the backbone of India’s growth strategy.
- Public capital expenditure continues at ₹12.2 lakh crore, nearly six times the 2014 level. An Infrastructure Risk Guarantee Fund will reduce construction-phase risks for private investors. CPSE land assets will be monetised through REITs.
- Connectivity initiatives include the new Dankuni–Surat Dedicated Freight Corridor, 20 new National Waterways starting with NW-5 in Odisha, and a Coastal Cargo Promotion Scheme to double shipping share by 2047.
- Seven high-speed rail corridors are planned across major economic regions. Seaplane manufacturing incentives and operational support will open regional air connectivity.
- City Economic Regions will promote decentralised urban growth in Tier II and III cities with ₹5,000 crore per region over five years.
- On clean energy, the Budget introduces a ₹20,000 crore CCUS mission across heavy industries, extends nuclear power customs exemptions till 2035, and supports battery storage and critical mineral processing.
This integrates growth, logistics efficiency and climate commitments.
#Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27. #Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27
5. MSMEs: From Survival to Competitive Scale
The focus now shifts from short-term relief to long-term enterprise strengthening.
A ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund will support high-potential firms. The Self-Reliant India Fund is topped up for micro enterprises.
TReDS reforms mandate CPSE participation, introduce credit guarantees and enable receivable securitisation for easier liquidity.
Corporate Mitras will provide affordable compliance support in smaller towns.
These reforms formalise MSMEs, improve access to capital and integrate them into national and global supply chains.
6. Social Sector, Skilling and Aspirational India
Human capital development emerges as a central growth driver.
- The healthcare workforce will expand through one lakh allied health professionals and 1.5 lakh trained caregivers annually. Trauma care capacity in district hospitals will rise by 50 percent. A new NIMHANS-2 institute and upgrades at Ranchi and Tezpur will strengthen mental health infrastructure.
- Five regional medical tourism hubs will be developed under PPP mode.
- Education reforms include an Education-to-Employment Standing Committee, AVGC content labs in 15,000 schools and 500 colleges, University townships near industrial corridors, and STEM hostels for girls in every district.
- Scientific research receives major infrastructure support through large solar telescopes, optical-IR facilities and space observatories.
- Sports development is integrated under the expanded Khelo India Mission.
#Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27
7. Agriculture, Fisheries and Rural Prosperity
The Budget shifts agriculture policy from volume production to income diversification.
- Bharat-VISTAAR will provide AI-based multilingual farm advisory integrating AgriStack and ICAR knowledge.
- High-value crop strategies focus on coconut rejuvenation, cocoa and cashew global branding, sandalwood cultivation, and region-specific crop clusters.
- Fisheries will expand through 500 reservoirs and Amrit Sarovars with coastal value chains led by women groups and startups.
- Livestock income will grow via credit-linked subsidies, veterinary colleges and Livestock FPOs.
- SHE-Marts will provide community-owned retail platforms for women SHG enterprises.
This approach multiplies rural incomes while improving climate resilience.
8. Tourism, Heritage and Regional Development
- Tourism is repositioned as a major employment and regional growth engine.
- Fifteen archaeological sites including Lothal, Dholavira and Rakhigarhi will become experiential destinations. A National Destination Digital Knowledge Grid will document cultural assets.
- Eco-tourism trails will promote mountain, turtle and bird-watching circuits. Buddhist heritage circuits in the Northeast will strengthen cultural diplomacy.
- The Purvodaya East Coast corridor will integrate industry, tourism and electric mobility.
- Hospitality education will be strengthened through a National Institute of Hospitality and large-scale guide training programmes.
- The Global Big Cat Summit will reinforce wildlife conservation leadership.
#Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27
9. Financial Sector Reforms
- Structural reforms aim to mobilise long-term growth finance.
- A High-Level Banking Reform Committee will review the sector. Power Finance Corporation (PFC) and Rural Electrification Corporation (REC)restructuring will enhance public NBFC efficiency.
- Corporate bond market liquidity will improve through market-making frameworks and total return swaps.
- Municipal bond incentives will strengthen urban infrastructure finance.
- FEMA rules will be modernised, and overseas Indians will gain greater equity investment access.
10. Tax and Regulatory Transformation
- Direct tax reforms include the new Income Tax Act effective from April 2026, simplified compliance, reduced TCS on foreign remittances, decriminalisation of offences, MAT rationalisation, buyback taxation reform, F&O STT hikes, startup and cloud incentives, and a new crypto compliance framework.
- Indirect tax reforms focus on customs simplification, critical mineral and battery incentives, lifesaving drug exemptions, export facilitation, SEZ relief measures, AI-based port scanning and integrated customs IT systems.
- Together, they aim tobuild a trust-based, low-friction compliance economy.
Union Budget 2026–27 transforms India’s growth model by blending fiscal discipline with industrial strength, human capital investment, infrastructure expansion and inclusive development—laying foundations for a resilient, innovation-driven Viksit Bharat.
#Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27 #Budget 2026-27
For more such preparation strategies, you can read here: https://laex.in/category/preparation-strategy/
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ Youtube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar : 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040.
