Paper: GS – II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Global issues, Issue: The Kimberley Process.
Context:
The Kimberley Process (KP) is a multinational initiative established to govern the trade of ‘conflict diamonds’ rough diamonds used by rebel or insurgent groups to undermine legitimate governments. Initiated in May 2000 by southern African countries, it led to the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) in 2003.
- Today, the KP comprises 60 participants representing 86 countries, accounting for approximately 99.8% of global rough diamond production.
Key Highlights:
The Current Structure:
The KPCS is the mechanism to prevent the trade of conflict diamonds, enforced individually by KP participant countries. Key features include:
- KP Certificates: Each consignment of rough diamonds must be accompanied by a KP certificate corroborated by a participant country.
- Trade Restrictions: Trade is permitted only between certified KP members who comply with international standards.
- Statistical Data: Participant countries are obliged to share timely and accurate statistical data for diamond production and trade.
While Angola, Botswana, Canada, Congo, Namibia, and Russia account for over 85% of rough diamond production, India is a major importer, handling roughly 40% of global imports.
- As the world’s leading cutting and polishing hub, India re-exports polished diamonds to major markets like China, Hong Kong, Israel, the UAE, and the United States.
- This strategic position gives India unique leverage within the global diamond value chain.
Core Issues and Challenges:
Despite its success, the KP faces criticism and challenges:
- Narrow Definition of ‘Conflict Diamonds’: The current definition focuses solely on the financial link between rebel groups and governments, ignoring state-linked abuses, human rights violations, environmental harm, and illicit trade channels.
- Decision-Making Process: The KP’s decision-making process is subject to political veto, raising questions about its ability to effectively identify and address conflict diamonds.
- Effectiveness of Embargoes: The case of the Central African Republic demonstrates that embargoes without strong support measures can increase smuggling and violence.
- Lack of Inclusivity: There is a need for a more inclusive approach that addresses the full range of challenges faced by communities in diamond-producing regions.
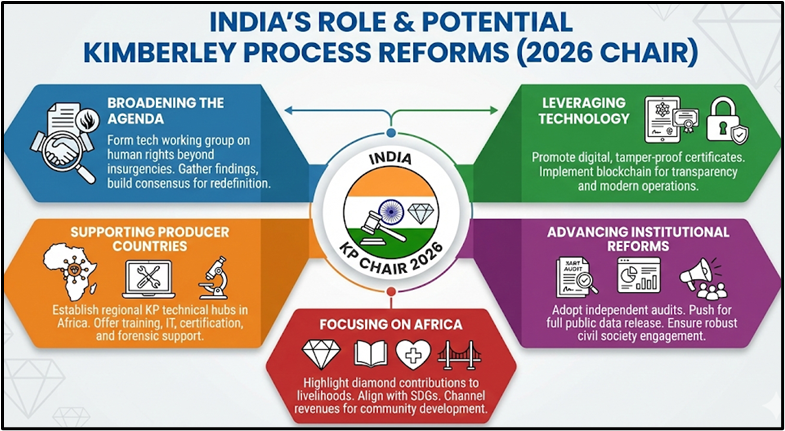
India, as the KP chair and a leader of the Global South, has a unique opportunity to pursue a reform agenda that makes the Kimberley Process a more inclusive, progressive, sustainable, and rule-based multilateral body. By addressing the core issues and implementing the proposed reforms, India can strengthen the KP and ensure a more responsible and equitable diamond trade that benefits communities and promotes sustainable development.
Source: (The Hindu)
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2026 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
