Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Achievements of Indians in science & technology
Issue: ISRO’s Fuel Cell
Context: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved a milestone by testing a fuel cell in space, utilizing hydrogen and oxygen to generate 180W of power.
Synopsis:
- The fuel cell, sent aboard the fourth stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) on January 1, produces heat and water as byproducts, making it suitable for human space missions.
- The fuel cell is a precursor to the future power systems for space stations, aligning with India’s goal of establishing a space station in low Earth orbit by 2035.
- The zero-emission cells demonstrated potential applications on Earth, possibly replacing vehicle engines. Another Silicon-based cell showcased during the mission offers a low-cost and lighter alternative to current cells.
- ISRO plans to incorporate these fuel cells in upcoming operational missions, anticipating a notable 35-40% battery mass saving. The cells’ resilience in harsh space environments was validated during the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM) flight.
- The fuel cell tests were part of 10 experiments on the January 1 PSLV launch, which included a radiation shielding experiment, an amateur radio, and three propulsion systems by space start-ups.
Background:
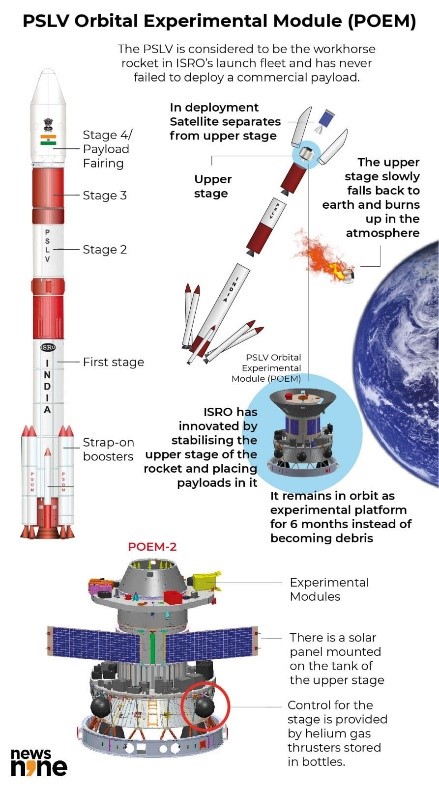
What Is POEM?
- POEM (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module) is an experimental mission by ISRO that performs in-orbit scientific experiments during the fourth stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) launch vehicle as an orbital platform.
- POEM has a dedicated Navigation Guidance and Control (NGC) system for attitude stabilization, which stands for controlling the orientation of any aerospace vehicle within permitted limits. The NGC will act as the platform’s brain to stabilize it with specified accuracy.
Conclusion: ISRO’s successful flight test of a 100W fuel cell, emitting only water, marks a significant step towards efficient power production in space and holds promise for emission-free transportation and space missions.

