Paper: GS – II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Federalism, Issue: The Federal Structure.
Context:
The Supreme Court of India’s response to the 16th Presidential reference concerning the powers of Governors and the President.
Key Highlights:
It argues that the Court’s interpretation undermines the core principle of federalism, potentially transforming States into subordinate entities dependent on the central government.
Federalism as a Vital Safeguard:
- Beyond Basic Structure: Federalism is not only part of the Constitution’s basic structure but also a vital safeguard against the central government’s arbitrariness and autocracy.
- Death Knell for Federalism: Undermining federalism could lead to the central government’s absolute dominion over institutions that seek to regulate and control its power.
Equal Partners in the Constitutional Scheme:
- Union and States as Equals: The Constitution envisions the Union and States as equal partners, with the central government being “first among equals,” not a superior authority.
- State Autonomy: States possess complete autonomy in areas within the State list, such as land laws and law and order.
- Violation of Constitutional Scheme: Any deviation from this understanding of federalism would disrupt the constitutional scheme envisioned by the framers.
The Role of Governors and the Threat to Democracy:
- Governor’s Actions: If Governors indefinitely delay Bills passed by State Legislatures or return them for reconsideration, only to reserve them for the President’s assent after reaffirmation, it undermines the elected Legislature.
- Governors as Central Appointees: Governors, often appointed by the ruling party at the Centre, may act on the central government’s whims and accommodate its political agendas.
Timelines and Reasonableness:
- Need for Timelines: A timeline for the Governor’s exercise of powers under Article 200 is necessary to align with the principle of federalism.
- Preventing Despotism: Without timelines, the Governor could become an unelected despot over an elected Government.
Judicial Review:
- Part of Basic Structure: “Judicial Review” is an essential part of the Constitution’s basic structure.
- No Immunity from Review: No authority, including Parliament, can claim immunity from judicial review.
- Accountability of Governors and the President: The offices of Governor and President should not be exempt from judicial review, as they are creations of the same Constitution.
Limited Direction and Constitutional Principles:
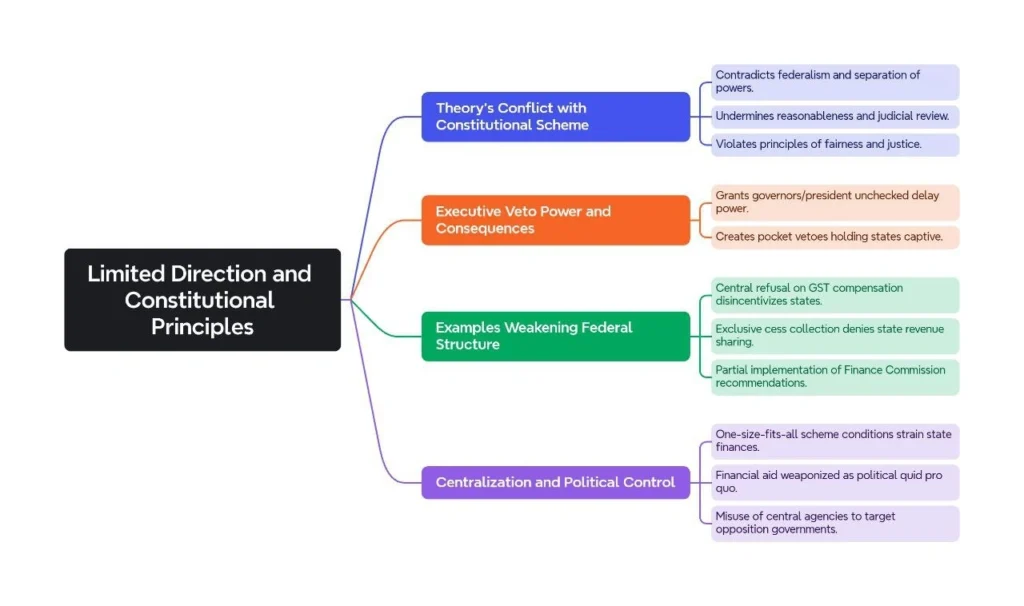
The presidential opinion may strengthen central control through Governors, threatening State autonomy. Safeguarding federalism requires limiting gubernatorial overreach and ensuring judicial oversight to protect democratic, constitutional balance.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
