Paper: GS – II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India’s relations with major powers, Issue: India-China-Russia triangular relations.
Context:
PM Modi’s meeting with Xi Jinping during the SCO Summit in Tianjin marks focus shift towards India–China–Russia dynamics amidst shifting global order. The key issue remains managing India–China relations without undermining India–U.S. strategic partnership.
Key Highlights:
India–China Engagement:
Diplomatic Nuance:
- Modi–Xi meeting symbolises attempts at normalisation.
- But structural challenges remain: border disputes, lack of trust, repeated stand-offs.
- History of setbacks:
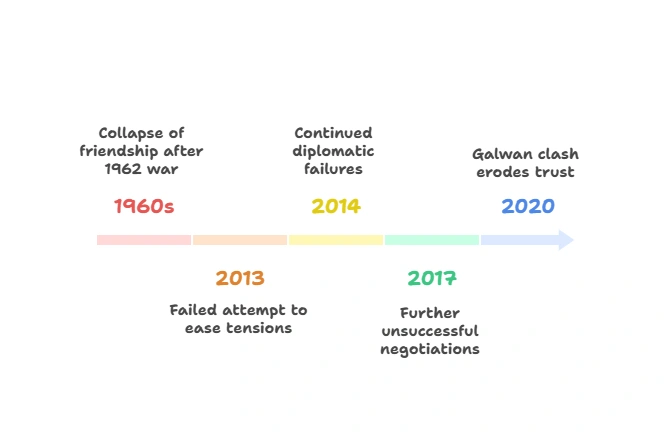
Persistent Contradictions:
- Rhetoric vs reality: Rhetoric of “partnership, non-rivals, Asian solidarity” masks deeper gaps.
- India’s policy dilemma: Balancing strategic autonomy with realities of border threats.
- Aggression tactics: China continues aggressive postures, undermining trust.
India–U.S. Factor:
- India’s growing alignment with U.S. overshadows its engagement with China.
- Strategic partnership with U.S. is carefully built over 3 decades.
- Current friction with U.S. especially over Russia and trade does not change India’s long-term alignment.
- India cannot underestimate the importance of Washington while engaging with Beijing.
Rebalancing and Equilibrium:
Lessons from History:
- India–China relations shaped not just by bilateral issues, but also external factors such as U.S., Russia, and global economy.
- Need to find balance between short-term tactical moves and long-term strategic interests.
- Need to overcome the past oscillations between cooperation and confrontation.
Modi–Xi Engagement in Tianjin:
- Seen as leap of faith and attempt to stabilise ties.
- Xi invoked Panchsheel Principles which signals continuity with older frameworks.
- But China’s actions such as border militarisation, economic coercion, “weaponisation of dependencies” create contradictions.
Contemporary Challenges:
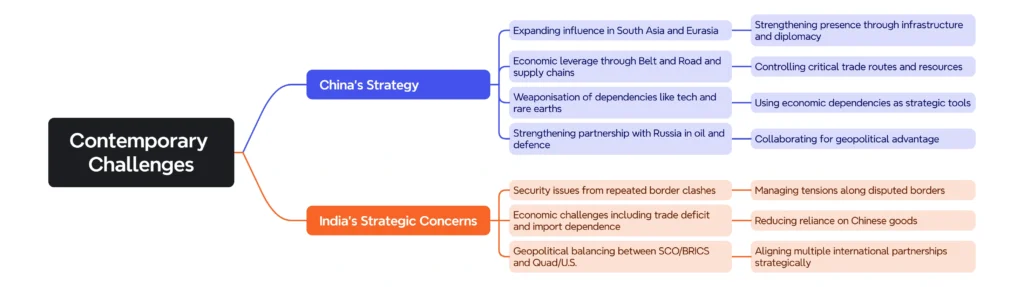
India’s Strategic Choices:
- Do not overestimate: Possibilities with China.
- Do not underestimate: Necessity of U.S. partnership.
- Maintain strategic autonomy, but strengthen trusted partnerships.
- Balance tactical engagement with China and strategic convergence with U.S. & allies.
Conclusion:
India–China relations remain fragile, tactical, and vulnerable to shocks. Trust deficit persists despite summitry and dialogue. India must pursue a careful balancing strategy engage China through SCO/BRICS, strengthen strategic partnerships with U.S., Japan, EU and preserve autonomy while ensuring security, stability, and economic resilience.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
