Paper: GS – II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Judiciary, Issue: Anti-Defection Law (ADL).
Context:
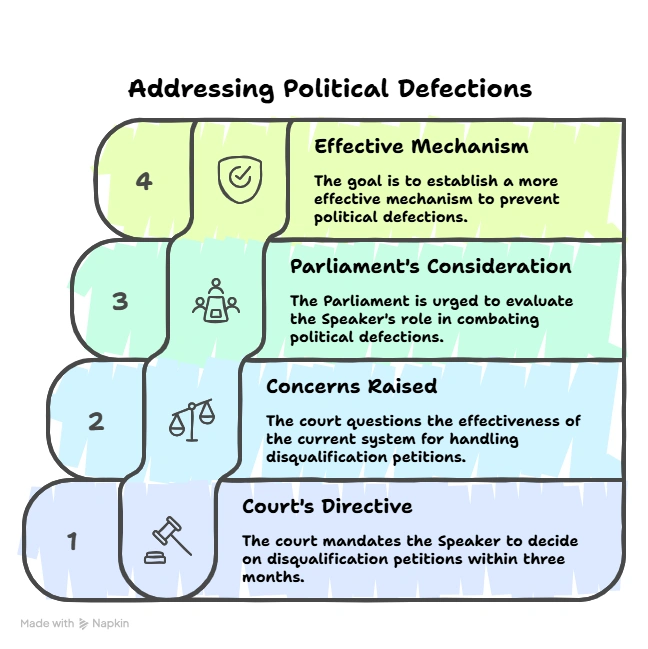
The Supreme Court’s directive to the Telangana Assembly Speaker regarding the disqualification petitions filed against 10 BRS MLAs who defected to the Congress party after the November 2023 elections.
Key Takeaways:
What is Defection?
- Defection, in a political context, refers to the act of a member of a legislative body, such as a parliament or state assembly, abandoning their affiliation with one political party, on whose ticket the member was elected, to join another political party.
- This often involves a shift in loyalty for personal gains, such as the promise of a position of power or other benefits. Along with breaching the trust of the electorate, defection can undermine the stability of governments and hence the governance processes.
What is Anti-Defection Law (ADL)?
The Anti-Defection Law (ADL) in India is a legal framework that seeks to curb the practice of political defection by members of the legislature, with the goal of promoting political stability and maintaining party discipline.
- Its primary aim is to deter the Members of Parliament and Members of State Legislatures from switching parties or voting against their party’s directives by imposing the threat of disqualification.
Constitutional Provisions Regarding Anti-Defection Law (ADL):
- The Anti-Defection Law (ADL) in India was introduced through the 52nd Amendment Act of 1985.
- It added the Tenth Schedule to the Indian Constitution, which contains the provisions related to the Anti-Defection Law.
- Later, the 91st Amendment Act of 2003 made some changes to certain provisions of the Anti-Defection Law (ADL).
- This entire development has been described in the following section.
52nd Amendment Act of 1985:
- The 52nd Amendment Act of 1985 provided for the disqualification of the Members of Parliament and the State Legislatures on the grounds of defection from one political party to another.
- To facilitate this, the Act made changes to four articles of the Indian Constitution: Article 101 and Article 190, which deal with the Vacation of Seats by Members of Parliament and Members of State Legislatures respectively.
- Article 102 and Article 191, which pertain to Disqualification from Membership of Parliament and State Legislatures respectively.
- Additionally, the Act added a new schedule, the Tenth Schedule, to the Indian Constitution.
- Thus, the 52nd Amendment Act is often referred to as the ‘Anti-Defection Law’.
Tenth Schedule (10th Schedule):
- It contains provisions related to the disqualification of Members of Parliament (MPs) and Members of State Legislatures (MLAs) on the grounds of defection.
- The Tenth Schedule lays down the circumstances under which a legislator can be disqualified from holding office if they violate certain conditions, such as voluntarily giving up their membership of a political party or voting against their party’s official stance on certain matters.
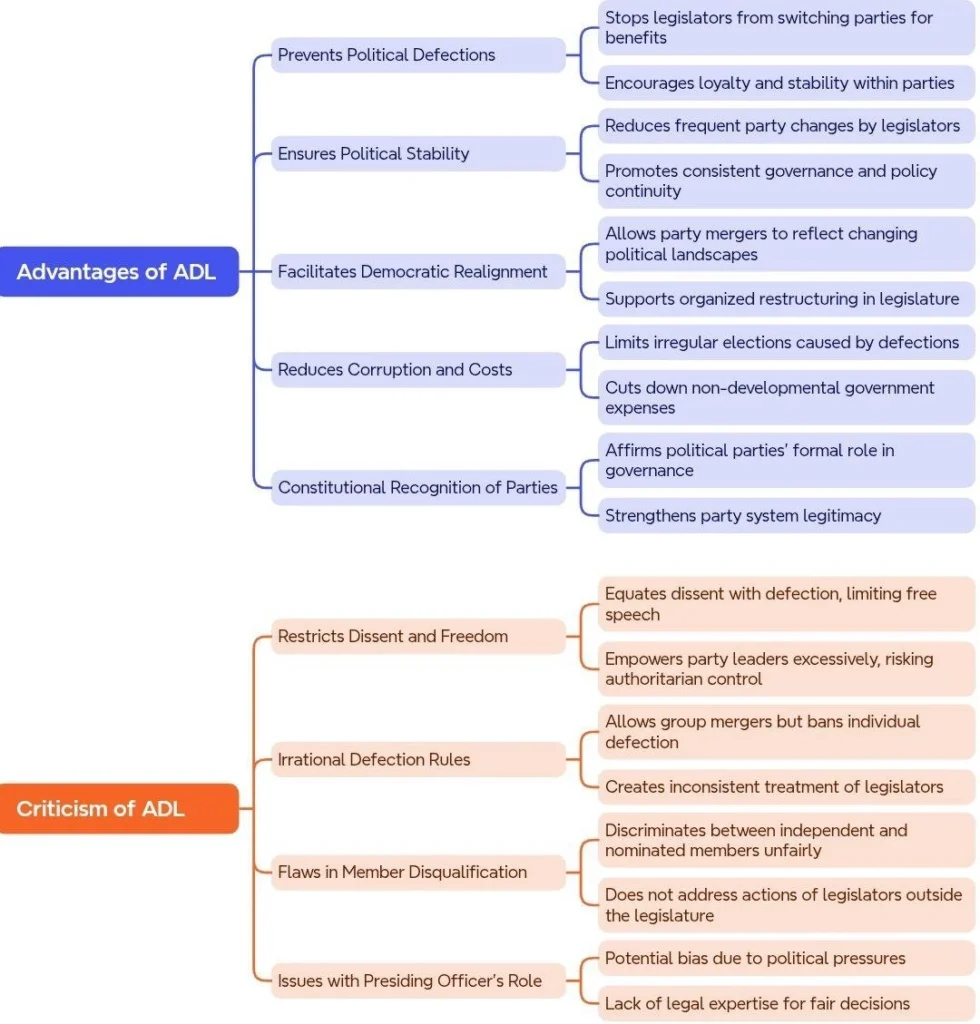
Anti – Defection Law in India:
Conclusion:
The Supreme Court’s ruling is a significant step towards ensuring accountability in political processes related to disqualification due to defection. However, it also raises important questions about the relationship between judicial oversight and legislative authority, the potential for political maneuvering, and the need for broader reforms in the anti-defection legislation in India.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
