Paper: GS – I, Subject: Geography, Topic: Geo – Physical Phenomenon, Issue: Himalayan Disaster Events.
Context:
The recent torrential rain and flash floods in Dehradun, Uttarakhand that claimed at least 13 lives highlight the growing vulnerability of the Himalayan states to extreme weather events.
- With 192 mm of rain in just a few hours at Sahastradhara, rivers swelled beyond their capacity, sweeping away homes, shops, hotels, and even religious sites.
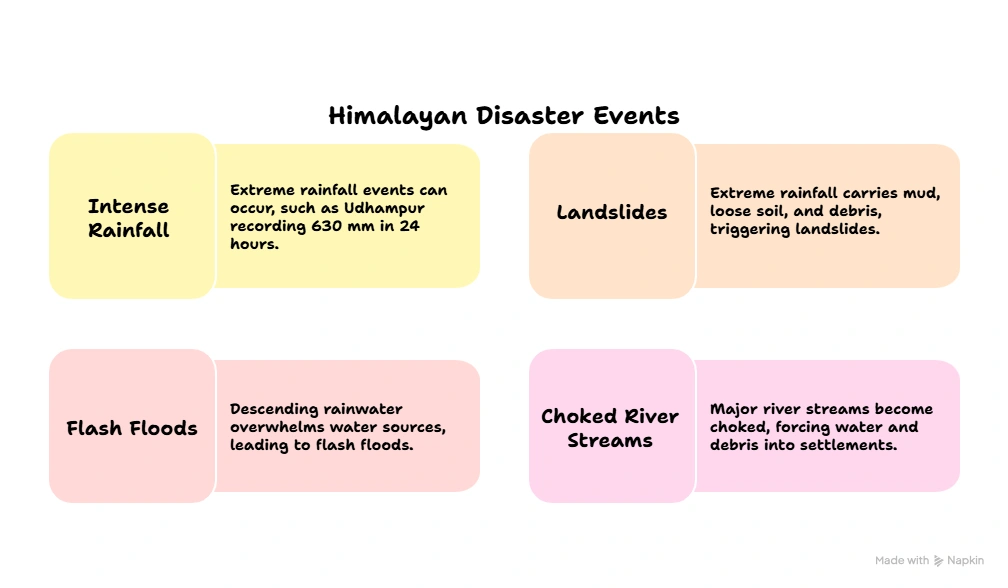
Key Takeaways:
Why Heavy Rainfall Hits Hard in the Himalayas:
- Topographic Influence: Steep mountain slopes mean rainfall drains rapidly downhill, carrying mud, soil, and debris, amplifying flash floods.
- Enclosed valleys choke stormwater flow, making riverbanks overflow into settlements.
- Active Monsoon Systems: Low-pressure systems from Bay of Bengal travel north, bringing intense rainfall to the northwestern Himalayan belt.
- In 2025 so far, northwestern India has had 30–67% excess rainfall, raising saturation levels in soil and rivers.
- Fragile Geology: Himalayan mountains are geologically young, prone to erosion. Heavy rain easily destabilises slopes, leading to landslides.
- Role of Climate Change: Southward shift of western disturbances interacts with strong monsoon systems, worsening rainfall unpredictability.
- Global warming increases likelihood of extreme rainfall events followed by prolonged dry spells.
- Melting Arctic ice further disrupts atmospheric circulation patterns, influencing monsoon behaviour.
Immediate Impacts of the Dehradun Floods:
- Loss of Lives and Injuries: 13 dead, 16 missing, several critically injured.
- Infrastructure Damage: Shops, hotels, roads, and bridges washed away; Tapkeshwar temple submerged.
- Disruption of Services: Jolly Grant airport and Mussoorie cut off temporarily due to heavy waterlogging.
- Evacuations: Over 500 students trapped in Paundha rescued; hotels in Mussoorie required emergency evacuation.
- Tourism Setback: Popular tourist spots like Sahastradhara and Mussoorie badly hit, damaging local livelihoods.
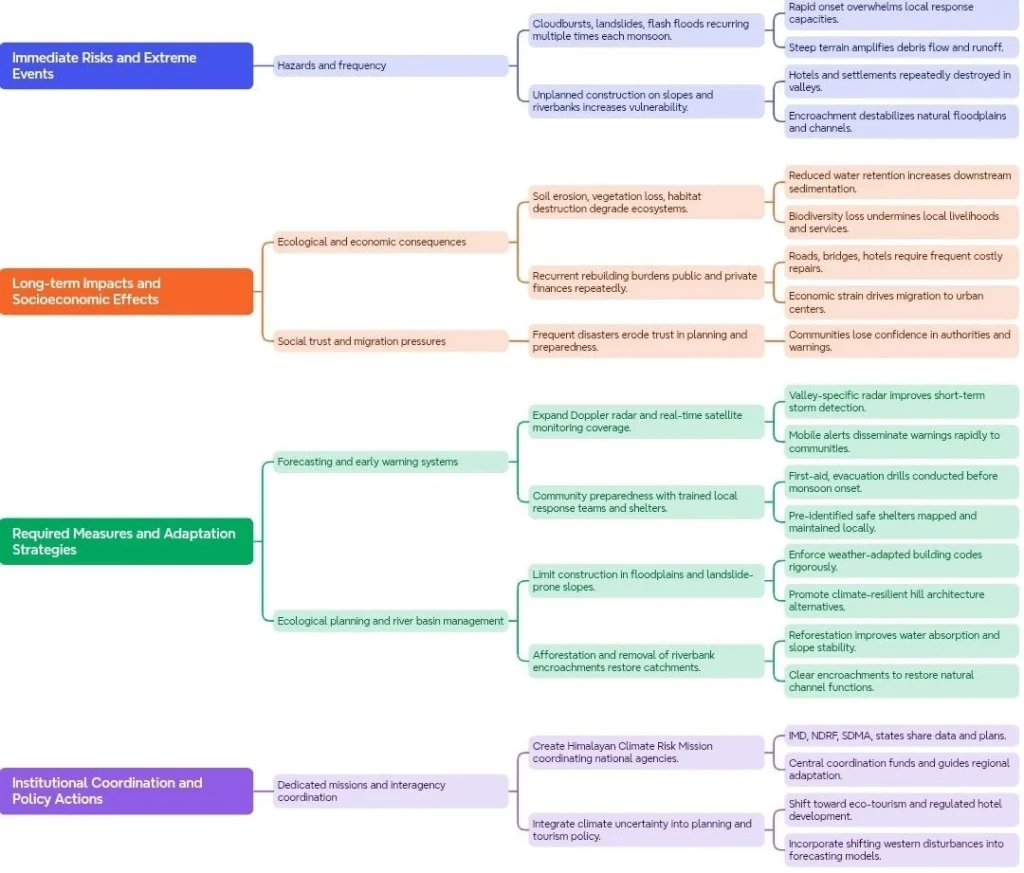
Broder Challenges in Himalayan States:
Conclusion:
The tragedy in Dehradun is a grim reminder that climate change, fragile Himalayan topography, and unchecked human activity are converging to intensify natural disasters. While the Himalayas will always remain vulnerable to extreme weather, scientific planning, strict regulation of land use, resilient infrastructure, and climate adaptation strategies can reduce risks.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
