Paper: GS – III, Subject: Society and Social Justice, Topic: Population and Associated Issues, Issue: Combating Antimicrobial Resistance in India.
Context:
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) has emerged as a major global public health threat due to overuse and misuse of antibiotics. According to the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), AMR was associated with ~2.67 lakh deaths in India in 2021.
Key Takeaways:
| What is AMR? Definition: AMR occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites evolve to resist antimicrobial drugs, rendering them ineffective. Impact: AMR complicates treatments, increases healthcare costs, prolongs illnesses, and risks lives globally. |
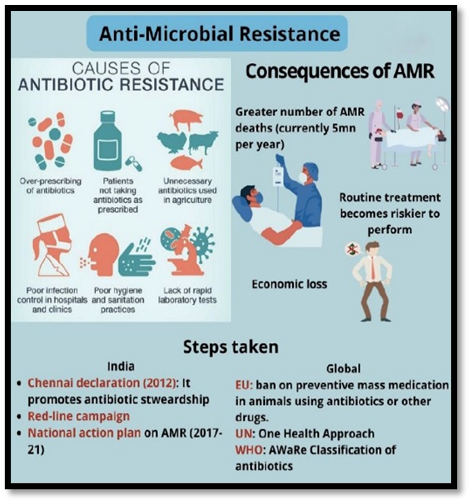
Why is the Antibiotic Pipeline “Running Dry”?
- Lack of Innovation: Very few new antibiotic classes discovered in the last two decades. Most approvals are modifications of existing drugs.
- Low Commercial Incentives: Antibiotics are short-course drugs low profitability. Pharmaceutical companies prefer chronic disease drugs.
- Rapid Resistance Development: New antibiotics lose effectiveness quickly due to misuse.
- Regulatory & Research Challenges: High R&D costs, long approval timelines.
Behavioral Aspects of Antibiotic Overuse:
- A learned behavior exists in India where people immediately resort to antibiotics for common ailments like coughs, colds, and diarrhea.
- Lack of awareness about the ineffectiveness of antibiotics against viral infections contributes to misuse.
Antibiotic Use in Livestock, Agriculture, and the Environment:
- The attributable risk to humans from antibiotics used in animals needs to be determined.
- High resistance levels in humans are often linked to antibiotics primarily used in human medicine, suggesting human behavior as the main driver.
- ICMR studies found a significant overlap of antibiotic resistance genes between human and environmental isolates from hospital surroundings, but minimal overlap between human and animal isolates.
Key Highlights:
| Section | Main points | Examples / Notes |
| Effectiveness of Antibiotic Stewardship | Antibiotic stewardship programs (rational prescribing – awareness) are more effective than outright OTC bans. A gradual, stepwise approach works best. Responsible-use mindset must be internalized. | Kerala model: Started with stewardship → later implemented OTC bans successfully. Emphasis on understanding “why” antibiotics must be used carefully. |
| Challenges in Treating Routine Infections | Drug-resistant infections need “next-level” antibiotics, increasing treatment complexity. Community infections are becoming complicated due to misuse. Misuse threatens effectiveness of important drugs. | UTIs: increasing complications. Typhoid: Salmonella typhi developing fluoroquinolone resistance. Overuse of ceftriaxone and azithromycin risks losing them for typhoid treatment. |
| Challenges in Data Collection | ICMR data is limited to 25 tertiary hospitals with strong microbiology labs—may not represent India. Tertiary hospitals often show higher resistance due to prior hospitalization/antibiotic exposure. | Proposed approach like Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (collects from 2,000 hospitals). |
| Alternative Therapies to Beat AMR | Phage therapy is promising (especially for UTIs), but needs precise matching; phage resistance can develop, so cocktails may be needed. Monoclonal antibodies are another option but still early-stage. | Phage therapy needs correct phage identification; resistance can occur → use virus cocktails. Monoclonal antibodies: research/early development stage. |
Antimicrobial resistance threatens modern healthcare by making routine infections difficult to treat. Effective antibiotic stewardship, improved surveillance, behavioural change, and a One Health approach are essential to preserve drug efficacy and public health.
Source: (The Indian Express)
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2026 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
