Paper: GS – II, Subject: Governance, Topic: Important aspects of governance, Issue: Upcoming census.
Context:
The 2027 Census introduces full digital enumeration with geo-tagging of all buildings, raising concerns over privacy, data security, digital divide, and citizen trust in governance.
Key Takeaways:
Historical Context:
- 1872: First population census conducted in India.
- 2011: Last Census (15th nationwide, 7th post-Independence) recorded 1.21 billion population, 330.84 million houses.
- 2021 Census: Postponed due to COVID-19, delayed by 6 years.
- Geo-tagging in India: Applied under schemes like Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (PMAY), MGNREGA assets, etc. for accountability.
- 2027 Census: First fully digital Census – includes self-enumeration, caste enumeration (first time since 1931), and geo-tagging of every building.
What is Geo-Tagging?
- Process of assigning latitude & longitude coordinates to a physical asset/building/location.
- Integrated with GIS (Geographical Information System) for precise mapping.
- Provides each building with a unique locational identity.
Geo-Tagging in Census 2027:
- Phase: To be conducted during Houselisting Operations (HLO), April–Sept 2026.
- Method:
- Enumerators will use smartphones (GPS-enabled) for geo-tagging via Digital Layout Mapping (DLM).
- Each building within a Houselisting Block (HLB) will be geo-tagged and classified:
- Residential
- Non-residential
- Partly residential
- Landmark
- Departure from the past: Earlier censuses relied on hand-drawn notional maps shifted now to digital maps auto-generated from geo-tagged data.
Benefits of Geo-Tagging in Census:

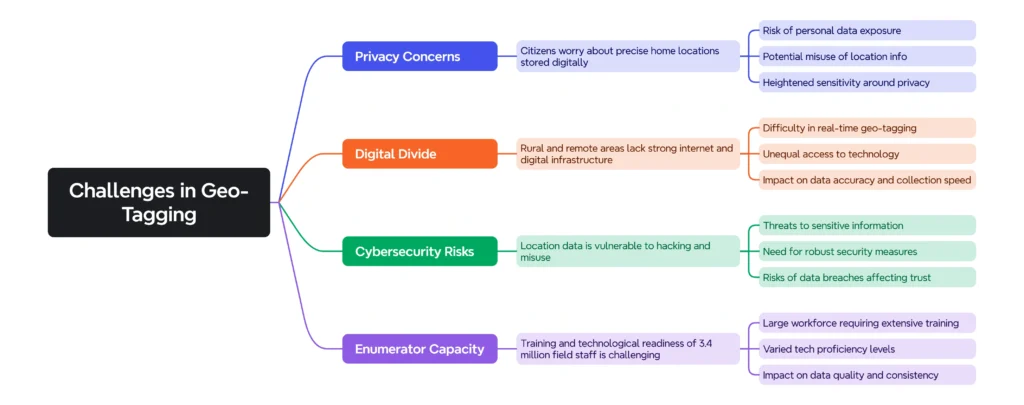
Challenges in Geo-Tagging:
Significance of updated census:
- Moves India closer to e-governance & evidence-based policymaking.
- Helps in achieving SDG 16.6 (effective, accountable, and transparent institutions).
- Provides reliable housing, demographic & socio-economic data for schemes like PMAY, Jal Jeevan Mission, Swachh Bharat, etc.
Way forward:
- Digital-first Census: Establishes baseline for all future censuses.
- Data Integration: Scope for linking with Aadhaar, land records, and urban planning databases.
- Public Trust: Must ensure data protection, anonymisation, and consent frameworks.
- Inclusivity: Training for enumerators + digital literacy for citizens critical for success.
Conclusion:
The geo-tagging of buildings in Census 2027 marks a paradigm shift in India’s governance model — from hand-drawn notional maps to real-time GIS-based digital maps. While it strengthens accuracy, transparency, and policy relevance, addressing privacy, digital divide, and data security will be crucial for its credibility and acceptance.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/how-geotagging-buildings-help-census-10242031/
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
