Paper: GS – II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Legislature, Issue: Parliamentary Panel Flags Safety Gaps in Charter Aviation.
Context:
A Parliamentary Standing Committee warned of safety gaps in India’s civil aviation especially in private and charter aircraft highlighting weak oversight, maintenance, and operational control in non-scheduled aviation, along with capacity constraints in the DGCA and ATC and the need for stronger industry-wide safety measures.
Key Takeaways:
Parliamentary Committees:
A Parliamentary Committee means a committee that:
- Is appointed or elected by the House or nominated by the speaker/Chairman.
- Works under the direction of the Speaker/ Chairman.
- Presents its report to the House or to the Speaker/Chairman.
- Has a secretariat provided by LS/RS.
Note: The appointment, Terms of office, functions and procedure of conducting business are regulated as per rules made by the two Houses under Article 118(1) of the Constitution.
| About Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA): India’s apex civil aviation regulatory body, responsible for overseeing air safety, licensing, and compliance with international standards. Established in: Originally set up in 1978 as an attached office of the Ministry of Civil Aviation. It became a statutory body under the Aircraft (Amendment) Act, 2020. Ministry: Operates under the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India. Objective: To promote safe, efficient, and secure air transportation through robust regulation and proactive safety oversight. |
Key Concerns Raised by the Parliamentary Standing Committee:
- Oversight lagging behind growth: Rapid expansion of charter and corporate aviation has outpaced safety supervision and enforcement capacity.
- Non-scheduled operators under scrutiny: Concerns over weak maintenance standards, poor documentation, and lean technical/safety teams.
- Need for stronger surveillance: DGCA must increase surprise inspections and tighten audit cycles for non-scheduled operators.
- Safety Management Systems (SMS): Mandatory, fully functional SMS needed for all private operators, on par with scheduled airlines.
- Flight planning & weather assessment: Risk evaluation, planning, and real-time oversight should not be diluted for non-scheduled flights.
- DGCA capacity constraints: Manpower shortages force reactive regulation; strengthening staffing, training, and data-driven oversight is essential.
- ATC capacity stress: High traffic loads without adequate staffing raise fatigue and human-error risks.
- Learning from past crashes: Safety recommendations must be monitored for actual implementation through a centralized mechanism.
- Smaller airport infrastructure gaps: Runways, navigation aids, and emergency response systems need upgrading alongside traffic growth.
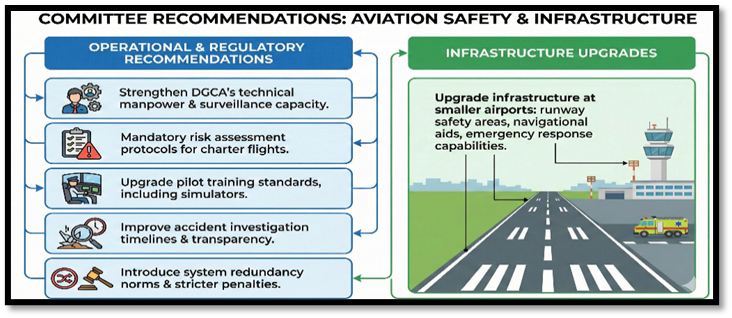
The Parliamentary Standing Committee’s report serves as a warning that India’s rapid aviation growth must be matched with a strong emphasis on safety. The report highlights specific areas of concern within the private and charter aircraft segment and provides recommendations for improving oversight, safety management, and infrastructure to mitigate systemic risk.
Source: (The Indian Express)
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2026 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
