Paper: GS – II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India Relations with Other Nations, Issue: India-Philippines Relations.
Context:
India and the Philippines have elevated their relationship to a strategic partnership, aiming to strengthen defence and maritime cooperation, launch direct flights, and negotiate a new trade agreement, as announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
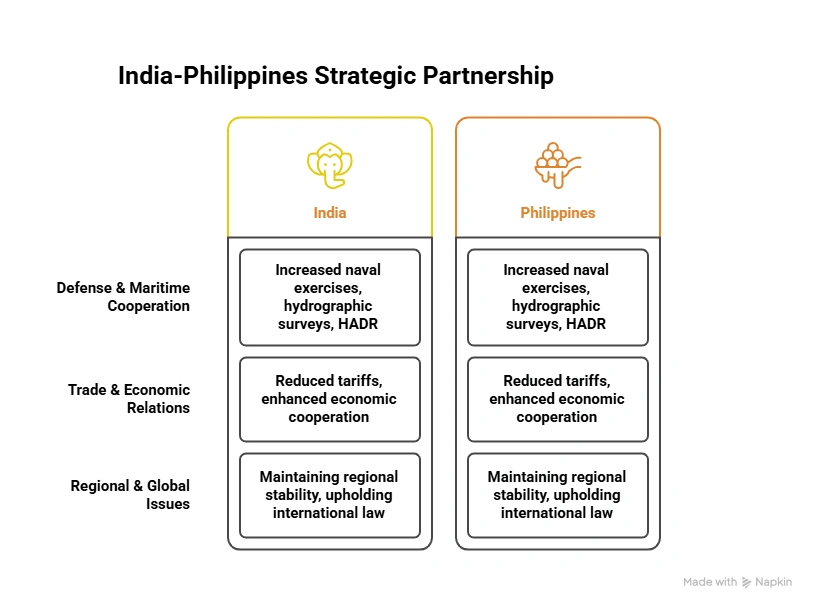
Key Takeaways:
What are the main outcomes of the recent India-Philippines bilateral talk?
- Strategic Partnership: India and the Philippines formalized a Strategic Partnership, reflecting India’s growing focus on Southeast Asia and its ‘Act East’ Policy.
- Indo-Pacific Engagement: India emphasized its commitment to a free, open, and rules-based Indo-Pacific, align with “MAHASAGAR” (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions) vision.
Defence cooperation:
- Naval Exercises: In August 2025, for the first time, Indian Navy participated in exercises in the Philippines.
- Defence Procurement: Discussions on defence acquisitions, including the BrahMos missile system.
- Maritime Domain Awareness: India invited the Philippines to participate in the Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR).
Economic partnership:
- Trade Liberalization: India to the review of the India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and agreed to work towards a bilateral Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA).
- Digital Economy: India offered to support a pilot project for the Philippines’ Sovereign Data Cloud Infrastructure.
| Evolution of India-Philippines Relations: Early engagement (1949-early 1990s): Diplomatic relations were established in 1949. Both countries shared democratic ideals and a commitment to anti-colonialism and South-South cooperation. Philippines opened its embassy in New Delhi in 1959, India open embassy in Manila in 1962. A Treaty of Friendship was signed in 1952. Limited high-level interaction during the Cold War era due to differing foreign policy alignments. Deepening engagement (Post 1990s) India’s “Look East” policy (initiated in 1992) and “Act East” policy (since 2014) boosted engagement with ASEAN nations, including the Philippines. India became a Sectoral Dialogue Partner of ASEAN in 1995. The Agreement on Expansion of Trade was signed in 1996.The ASEAN–India Free Trade Area agreement, signed in 2009, also included the Philippines. In 2022, India and the Philippines signed a $ 375 million agreements for BrahMos supersonic cruise missile system. August 2025 meeting elevated ties to a Strategic Partnership. |
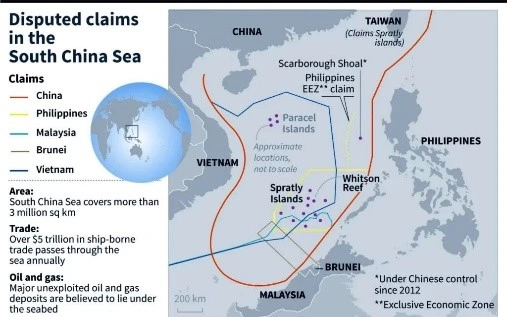
India’s Position on the South China Sea and Strategic Partnership with the Philippines:
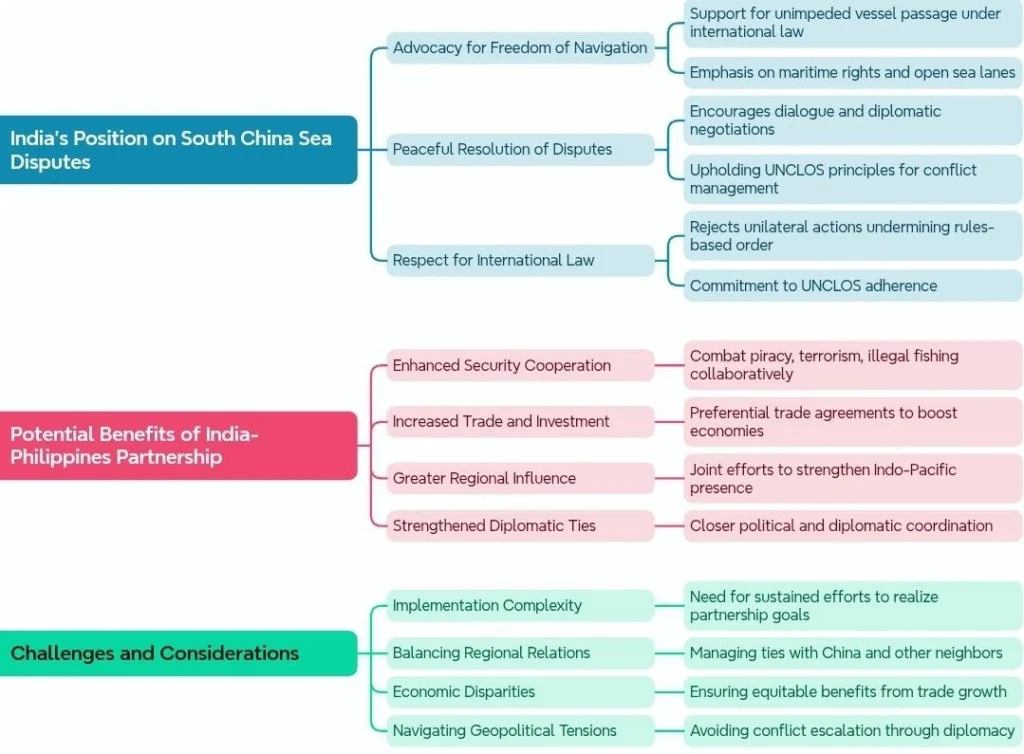
Conclusion:
By focusing on defense and maritime security, trade, and regional issues, the partnership has the potential to enhance security, boost economic growth, and promote regional stability. However, addressing the challenges and considerations outlined above will be crucial to ensuring the success of this enhanced partnership.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
