Paper: GS – I, Subject: Society and Social Justice, Topic: Population and Associated Issues, Issue: Phases of Census.
Context:
India is preparing for the 16th Census, beginning with the House-listing & Housing Census (HLHC) phase, scheduled April–September 2026. This will be followed by the Population Enumeration phase in February 2027.
- The exercise comes after a six-year delay since Census 2011, largely due to COVID-19 and administrative constraints.
Key Takeaways:
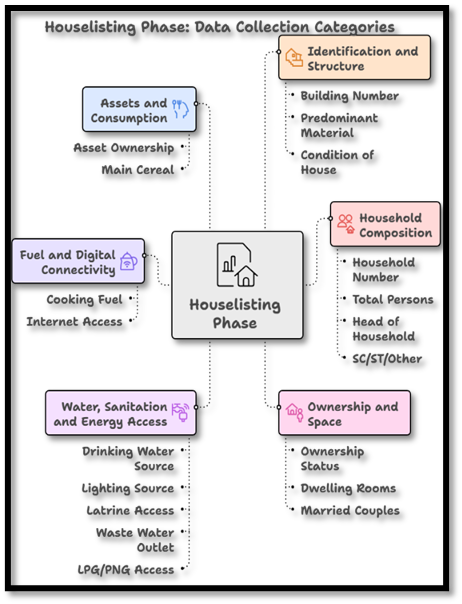
What is the House-listing & Housing Census?
- Purpose: To create a comprehensive inventory of all buildings, Census houses, and households across India.
- Focus: Captures information about where and how people live, unlike population enumeration which focuses on individuals.
- Process: Enumerators visit every structure (residential, commercial, or mixed-use).
- Outcome: Each household is assigned a unique Census house number and household number, forming the basis for individual enumeration.
- Additional Benefit: Allows the Registrar General of India (RGI) to assess housing conditions and household assets.
Significance: First nationwide Census exercise since 1931 to include major digital transformation.
Key Changes in Census 2027:
- Digital-first Enumeration: Enumerators will use mobile applications instead of paper schedules. Self-enumeration option via government portal for the first time.
- Use of GIS & Geo-tagging: Every Census house will be geo-tagged.
- Enables precise mapping, faster validation, and reduced duplication.
- Real-time Monitoring: Dashboards for supervisors under the Census Management & Monitoring System (CMMS). Enhances accountability and data accuracy.
Why is this Data Important?
- Policy Targeting: Supports schemes like PM Awas Yojana, Jal Jeevan Mission, Ujjwala, Swachh Bharat Mission, Digital India.
- Measuring Deprivation: Shift from “basic shelter” to connectivity, clean energy, and mobility.
- Evidence-based Governance: Enables granular planning at district and ward levels.
- Digital Divide Mapping: Internet access data helps refine e-governance delivery.
- Example: Internet access data can guide expansion of telemedicine, online education, and DBT platforms.
Challenges:
- Digital Literacy Gaps may affect self-enumeration.
- Data Privacy & Security concerns with large-scale digitisation.
- Last-mile connectivity issues in remote and tribal regions.
- Enumerator training and device availability.
Way Forward:
- Robust data protection protocols aligned with DPDP Act.
- Assisted self-enumeration for digitally excluded groups.
- Offline data collection modes with later syncing.
- Capacity-building of enumerators and local officials.
Source: (The Indian Express)
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2026 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
