Paper: GS – II, Subject: Polity, Topic: Judiciary, Issue: Tribunals Reforms Act, 2021.
Context:
Since 2017, India’s judiciary and Centre have clashed over tribunal autonomy, tenure, and appointments. The 2021 Reforms Act, reinstating struck-down provisions, has led to vacancies and delays.
Key Takeaways:
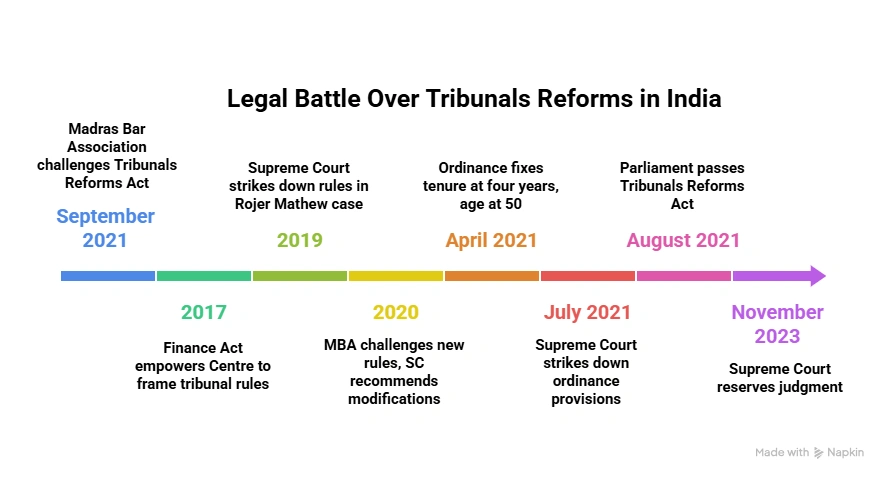
About the Tribunal Reforms Act, 2021:
- The Tribunals Reforms Act, 2021, enacted on 13 August 2021, seeks to streamline and rationalize tribunals by abolishing several appellate bodies and transferring their functions to High Courts.
- It replaces the Tribunals Reforms Ordinance, 2021, and consolidates provisions governing appointments, tenure, service conditions, and removal of tribunal members.
Aim:
- To reduce delay in justice delivery by integrating tribunal functions within the existing judicial structure.
- To ensure uniformity in appointments and service conditions across tribunals.
- To enhance administrative efficiency and judicial accountability by limiting executive interference.
Key Features:
- Abolition of certain tribunals: Eliminates appellate bodies such as the Film Certification Appellate Tribunal, Intellectual Property Appellate Board, and Airport Appellate Tribunal, transferring jurisdiction to High Courts.
- Centralised Appointments: Chairpersons and Members are appointed by the Central Government on the recommendation of a Search-cum-Selection Committee chaired by the CJI or his nominee.
- Tenure and Age Limits: Chairperson: 4 years or until 70 years of age. Members: 4 years or until 67 years of age.
- Minimum Age: Candidates must be 50 years or older for appointment, excluding younger professionals from consideration.
- Transitional Provisions: Members of dissolved tribunals cease office immediately and pending cases are transferred to High Courts.
- Power to Amend Schedule: The Central Government may, by notification, amend the list of tribunals covered under the Act.
Core Issues of Contention:
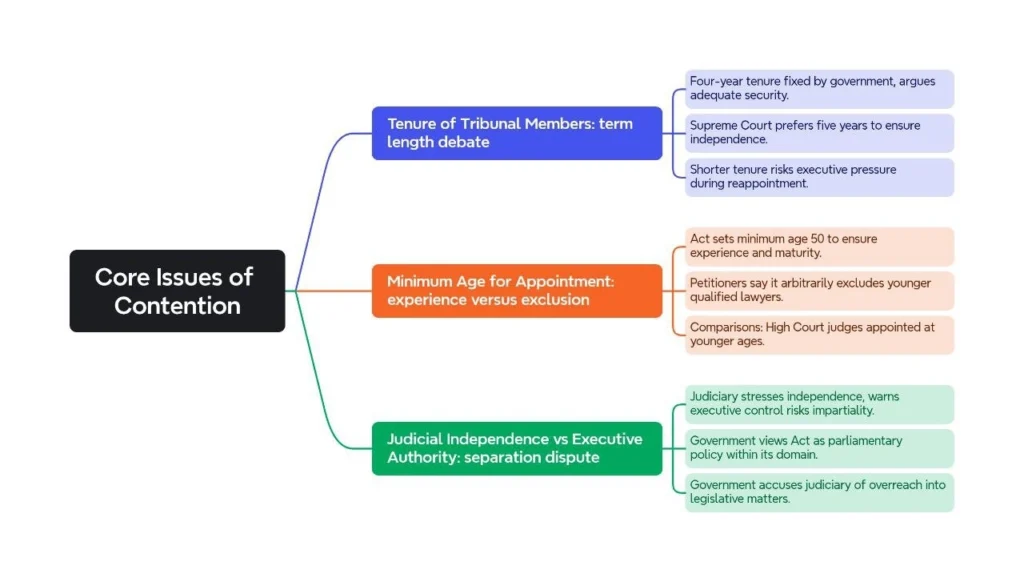
The conflict between the Supreme Court and the Centre over tribunals underscores deep differences on judicial independence and separation of powers, affecting tribunal functioning and dispute resolution, with the Court’s upcoming judgment holding lasting consequences for India’s tribunal system.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
