Paper: GS – II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: Global Issues, Issue: Thailand – Cambodia Relations.
Context:
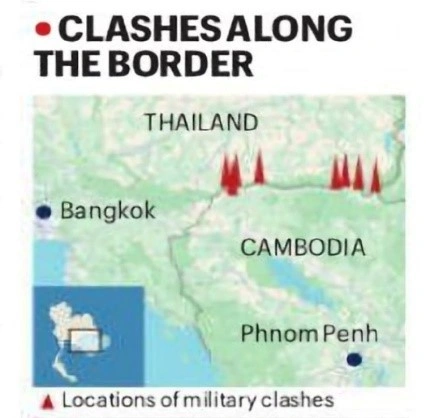
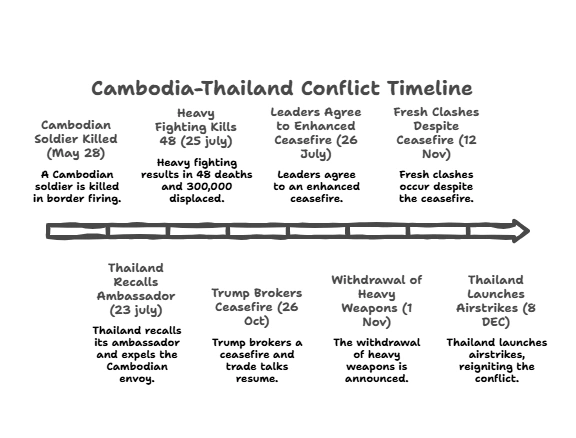
Thailand launched airstrikes on “military targets” in Cambodia after alleging that Cambodian troops killed two Thai soldiers along their disputed border. Cambodia denies initiating fire.
Key Takeaways:
This violence revives a long-running border dispute rooted in colonial-era demarcations.
Origins of the Border Dispute:
Colonial Boundary (1907):
- Border drawn by France (then administering Cambodia) and Siam (Thailand).
- Each country claims the map favoured the other.
- Disputes arise from inconsistent or contested colonial cartography.
Cultural-Historical Claims:
- Both predominantly Theravada Buddhist nations claim cultural ties to disputed regions.
- Each asserts being the “original” or “rightful” cultural owner, intensifying nationalistic tensions.
The Preah Vihear Temple:
- The epicentre of conflict; known as Preah Vihear in Cambodia and Phra Vihan in Thailand.
- Built in 11th–12th century under Khmer Empire; sits atop Dangrek Mountains along the border.
- Symbolic, religious, and strategic importance makes it highly sensitive.
After Independence – Why the Dispute Continued:
- Cambodia and Thailand dispute sovereignty over the temple despite a 1962, International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruling giving it to Cambodia.
- In 2008 tensions rose again when Cambodia sought UNESCO World Heritage status for the temple.
- Thailand objected, calling it a loss of Thai cultural identity and “territorial sovereignty.”
Current Crisis: Why the Conflict Flares:
- Highly nationalistic politics on both sides.
- Ambiguous historical claims due to colonial-era maps.
- Sharp troop presence near the temple area.
- Relatively weak dispute-resolution mechanisms within ASEAN.
- Each clash risks drawing both nations into wider conflict cycles.
BROADER IMPLICATIONS:
Regional Stability:
- Threatens peace in mainland Southeast Asia.
- Disrupts border communities, trade, and cross-border movement.
Colonial Legacy:
- Demonstrates how European-imposed borders continue to cause conflict in Asia.
- Shows long-term effects of ambiguous treaties and inconsistent mapping.
International Law:
- Thailand’s refusal to accept ICJ jurisdiction weakens international adjudication mechanisms.
- Highlights limit of global institutions when states assert sovereignty strongly.
The renewed Thailand–Cambodia clashes show how fragile ceasefires and unresolved colonial borders fuel recurring tensions. Without genuine dialogue, verified de-escalation, and stronger ASEAN mediation, the border will remain a persistent threat to regional stability and civilian safety.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
