Paper: GS – III, Subject: Internal Security, Topic: Challenges to Internal Security Through Communication networks, Issue: National IED policy.
Context:
The recent Red Fort blast, confirmed to be caused by a mixture of ammonium nitrate and triacetone triperoxide (TATP), underscores the persistent threat posed by IEDs in India.
Key Takeaways:
About Improvised Explosive Device:
- An IED is a type of unconventional explosive weapon that can take any form and be activated in a variety of ways.
- IEDs are used by criminals, vandals, terrorists, suicide bombers, and insurgents.
- Because they are improvised, IEDs can come in many forms, ranging from a small pipe bomb to a sophisticated device capable of causing massive damage and loss of life.
- The extent of damage caused by an IED depends on its size, construction, and placement and whether it incorporates a high explosive or propellant.
- The term IED came into common usage during the Iraq War that began in 2003.
Materials Used as Explosives in IEDs:
- Many commonly available materials, such as fertilizer, gunpowder, and hydrogen peroxide, are used as explosive materials in IEDs.
- Explosives must contain a fuel and an oxidizer, which provides the oxygen needed to sustain the reaction.
- A common example is ANFO, a mixture of ammonium nitrate, which acts as the oxidizer, and fuel oil (the fuel source).
Current Trends and Challenges:
Data from the National Bomb Data Centre of NSG indicates a declining trend in IED blasts across conflict zones and the hinterland. However, several concerning trends persist:
- Hybrid Explosives: Terrorist groups are increasingly using a mix of military-grade, commercial, and homemade explosives in IEDs.
- Cross-Border Smuggling: Military-grade explosives are often supplied by Pakistani handlers via drones or human couriers. Despite improved border management, the challenge remains in intercepting every consignment.
- Diversion of Commercial Explosives: Commercial explosives and detonators, used in mining and construction, are vulnerable to pilferage, especially in insurgency-prone areas.
- Homemade Explosives: While commonly used fertilizers in India have safeguards, precursor chemicals that can be used to extract explosives need stricter monitoring.
National Counter-IED Policy Framework:
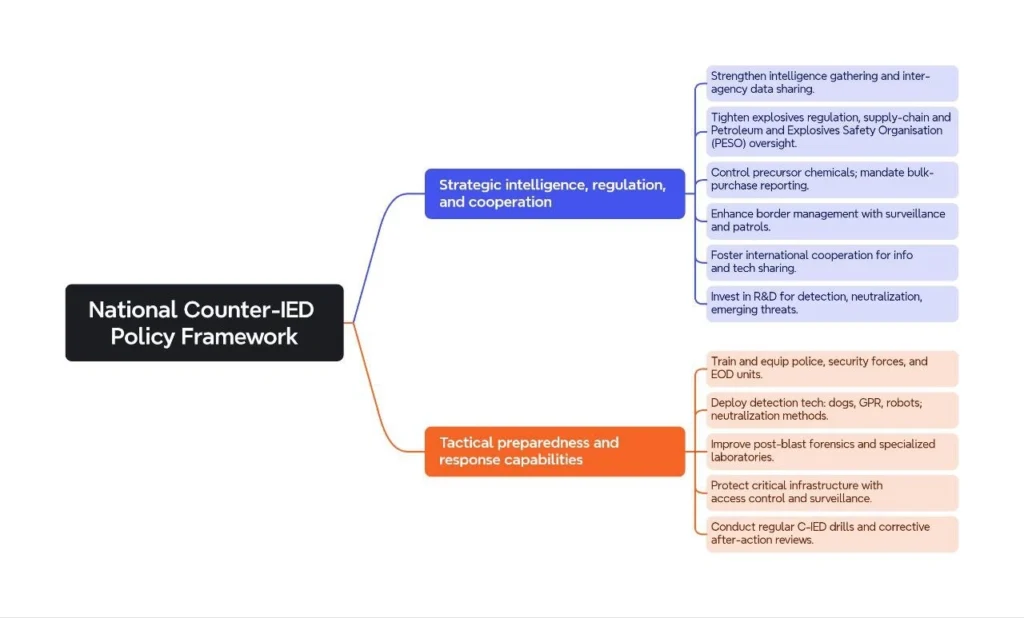
The threat of IEDs in India is real and evolving. A comprehensive National Counter-IED Policy is essential to effectively address this menace. The policy should be dynamic and adaptable to address emerging threats and technological advancements in IED fabrication and deployment.
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
