Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Economic Development
Topic: Growth, development, and employment.
Issue: K shaped recovery.
Context: SBI report disputes K-shaped recovery, shows income inequality decline in India, citing rising tax filings, consumption trends, and gender inclusivity.
Synopsis:
- SBI report disputes K-shaped recovery, asserts declining income inequality in India.
- ITRs show a 291% increase for earners between Rs 10 lakh and Rs 25 lakh.
- Total ITR filings rose to 7.4 crore in AY23 from 7 crore in AY22; 8.2 crore filed by Dec 2023.
- Female tax filers increased; suggests analysis for broader base.
- Consumption trends, Zomato data refute distress claims, show rising experience-centric income groups.
- Gini coefficient declines from 0.472 to 0.402 during FY14-FY22, indicating reduced income inequality.
- Migration to higher income brackets results in 21.3% additional income for 36.3% of taxpayers.
- Small firms transitioning, bottom 90% consumption post-pandemic rise by Rs 8.2 lakh crore.
- Decline in two-wheeler sales attributed to a shift towards four-wheelers and physical assets.
- Report challenges narratives, provides a comprehensive analysis of income trends, tax filings, and consumption patterns.
- Top of Form
Background:
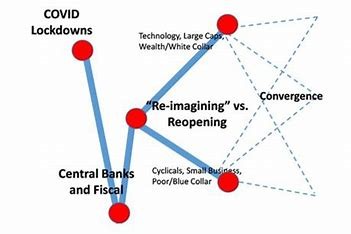
K-shaped recovery
- A diverging economic scenario where certain sectors of the economy will be thriving while other sectors will continue to decline or struggle to recover.
The thriving sector is represented in the upper part of K while the declining part of the economy is represented in the lower part of the K shape.
Conclusion: SBI report challenges distress narratives, revealing positive income trends, tax filings, and consumption patterns, affirming economic resilience.
