Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Achievements of Indians in science & technology
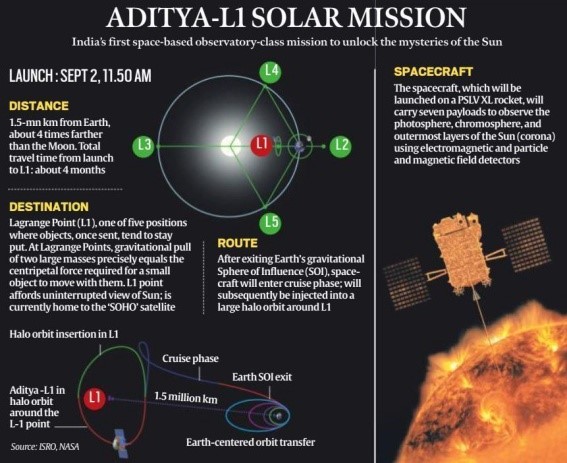
Issue: Aditya L1 Mission.
Context: The Aditya-l1 space probe executing its final manoeuvre on January 6 to enter a halo orbit around Sun-Earth Lagrange Point 1 (L1) 1.5 million km away, which was Launched on September2.
Top of FormSynopsis:
- Aditya-L1 is ISRO’s first space-based observatory to examine the Sun.
- Aims for a five-year mission to study the Sun and solar storms from L1’s unobstructed view.
- Equipped with seven instruments, it will provide crucial data on solar dynamics.
- L1 is an ‘unstable’ Lagrange point, requiring periodic makeovers to counter trajectory errors and maintain the intended orbit.
- Aditya-L1 joins four active probes at L1, including NASA’s WIND, ACE, DSCOVR, and ESA’s SOHO, enhancing solar observation capabilities.
- ISRO relies on precise “orbit determination” procedures using mathematical algorithms and specialized software for accurate positioning.
Objectives:
- Studying solar upper atmospheric dynamics,
- Coronal heating,
- Plasma physics, and
- Space weather drivers.
Challenges:
- Maintaining stability at Lagrange Point 1, requiring precise maneuvers.
- Continuous Adjustments are essential to counteract gravitational influences and ensure the correct orbit.Accurate “orbit determination” using algorithms and specialized software is vital for mission success.
- External gravitational forces from celestial bodies add complexity to maintaining the spacecraft’s designated orbit.
Background:
Conclusion: The success of this mission underscores ISRO’s capabilities in tackling complex space missions and advancing our understanding of the Sun.
