Syllabus: GS-III;
Subject: Disaster Management;
Topic: Disaster and Disaster Management.
Issue: Land Slides Map.
Synopsis:
- The map, called as ‘Indian Landslide Susceptibility Map’, is the first of its kind by virtue of being on a national scale, leaving out no locations in the country.
- Aim: To help identify the most dangerous areas and help allocate resources for mitigation strategies better
- The map data is available for free; an online portal has also been created.
- 5 lakh landslides data was collected via the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and other sources.
- Information was gathered from across the country on 16 such factors, like soil type, tree cover, which they called landslide conditioning factors.
- The researchers said they want to build on data from the map and develop a ‘Landslide Early Warning System’ for India.
Landslides: Landslides are the mass movement of rock, soil, and debris down a slope.
Various factors causing landslides include:
- Heavy rainfall: This is the most common trigger, as water seeps into the soil, increasing its weight and reducing its cohesion.
- Earthquakes:Seismic activity can destabilize slopes and trigger landslides.
- Erosion:Undercutting of slopes by rivers or streams can weaken the support and lead to landslides.
- Changes in groundwater levels:Rapid decreases or increases in groundwater levels can destabilize slopes.
- Human activities: Deforestation, improper construction practices, and mining can all increase the risk of landslides.
Effects: Impact on the economy, damages to infrastructure, loss of life, disruption of landscapes, decline in river ecosystems, trigger floods, affect livelihoods, and impede development
Vulnerability zones:
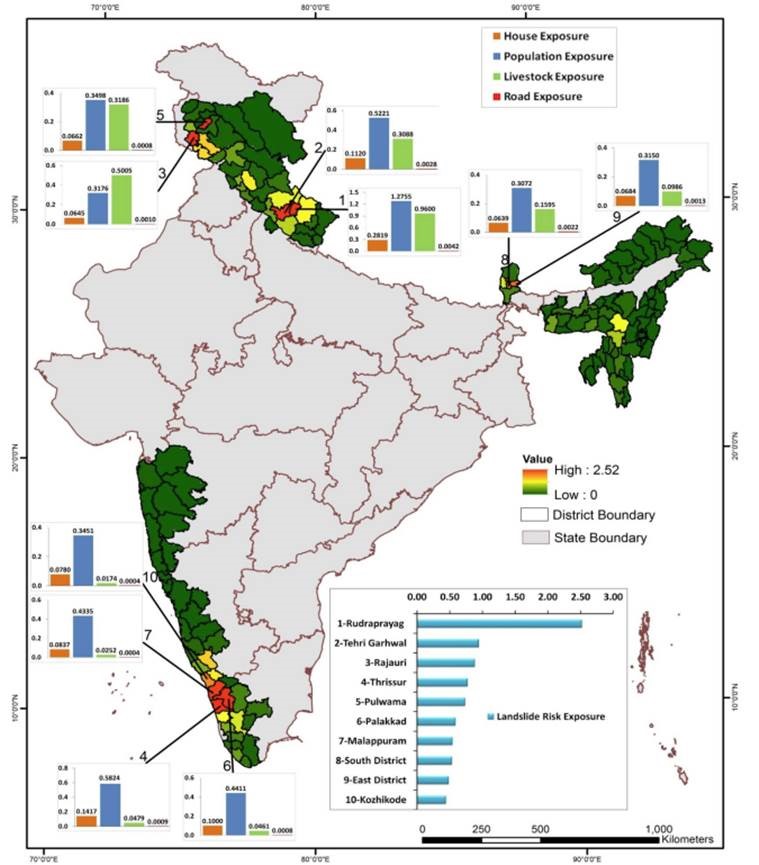
Landslides happen in very localised areas and affect only about 1-2% of the country.
- The spread of landslides in India is not uniform.
- Himalayan region – most affected.
- The Northeastern states – highly prone
- The Western Ghats states – regular landslides.
National Initiatives:
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA): Mandated to formulate policies and guidelines for disaster management.
National Landslide Risk Management Strategy: Task Force with sub-groups addressing hazard maps, monitoring systems, awareness programs, capacity building, regulations, and stabilization/mitigation.
Conclusion: This landslide vulnerability map marks a significant step forward in proactively mitigating the risk of landslides and protecting communities. By identifying areas susceptible to landslides, this map can inform crucial preventative measures, saving lives and minimizing property damage.
