CAR-T CELL THERAPY
Why in news?
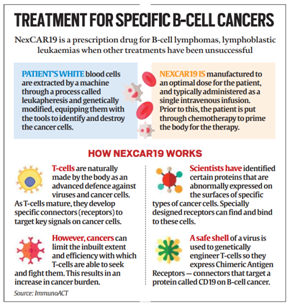
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has approved NexCAR19, an Indian CAR-T cell therapy developed by ImmunoACT, an IIT Bombay incubated company.
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy?
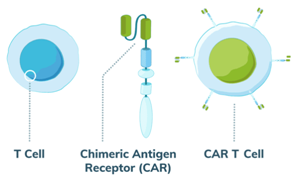
- CAR-T cell therapy modifies T-cells into potent cancer fighters.
- T-cells are a type of white blood cell that typically fights infections.
- In CAR-T therapy, these T-cells are genetically modified to target cancer. This makes them more effective, and they are called “living drugs.”
How Do CAR-T Cells Kill Cancer Cells?
- The therapy is made to attack cancer cells with the CD19 protein. This protein acts as a marker on cancer cells, allowing CAR-T cells to identify and attach to them, starting the process of eliminating the cancer.
- They primarily target and destroy cancer cells, particularly in blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphomas.
Mechanism:
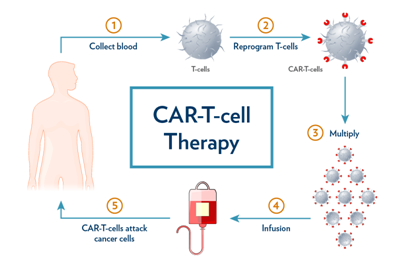
- Collection: T cells (a type of immune cell) are extracted from the patient’s blood through a process called leukapheresis.
- Genetic modification: In the laboratory, these T cells are genetically engineered to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific to a protein found on the surface of cancer cells.
- Expansion: The modified CAR-T cells are cultured and expanded to create a large population of these specialized cells.
- Infusion: The expanded CAR-T cells are then infused back into the patient’s bloodstream.
- Targeting cancer cells: The CAR on the surface of these engineered T cells allows them to recognize and bind to the cancer cells that express the corresponding antigen.
- Activation: Once bound to the cancer cells, the CAR-T cells become activated and initiate an immune response against the cancer cells.
- Killing cancer cells: The activated CAR-T cells release cytotoxic substances and trigger an immune response, leading to the destruction of the cancer cells.
- Persistence: Some CAR-T cells may persist in the patient’s body, providing long-term surveillance and potential protection against cancer recurrence.
| India is one of the first developing countries with its own CAR-T and gene therapy capabilities. This allows the therapy to be sold in India at a much lower cost than abroad. |
The benefits of CAR-T cell therapy:
- High efficacy in treating certain blood cancers.
- Targeted treatment with minimal harm to healthy cells.
- Potential for long-lasting protection.
- Curative potential.
- Personalized for each patient.
- Reduced need for chemotherapy.
- Ongoing research for broader applications.
Issues and Challenges associated with CAR-T cell therapy:
- Severe Immune Response: CAR-T therapy can trigger a strong immune response called CRS, which can be very harmful.
- Brain and Nervous System Effects: Some patients may experience confusion or seizures.
- Limited Use: It’s currently only approved for specific blood cancers, not solid tumours.
- High Cost: It’s often very expensive and not affordable for many patients.
- Complex Manufacturing: Making CAR-T cells is complex and time-consuming, causing treatment delays.
- Unknown Long-Term Effects: We’re still learning about the therapy’s long-term results.
- Target Loss: Some cancer cells can lose the CAR-T target, reducing its effectiveness.
- Overactive Immune Response: Sometimes, the immune system can harm healthy tissues due to its aggressiveness.
- Limited Access: Not all hospitals provide CAR-T therapy, and it’s not widely available.
- Ongoing Research: More studies are needed to treat a wider range of cancers and make CAR-T therapy safer and better.
TERMINOLOGY:
Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO):
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) is India’s national regulatory body for cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and medical devices. It works under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India.
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs):
CARs are special receptors that change how T cells work. They help T cells target specific things in the body’s immune response.
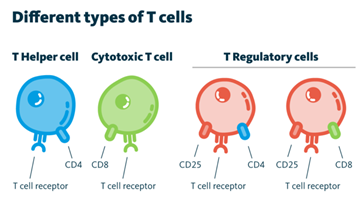
T-Cells:
T cells, or T lymphocytes, are white blood cells which are crucial for the immune response.
There are two primary types: Helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells.
- Helper T cells support other immune cells.
- Cytotoxic T cells are responsible for killing virally infected cells and tumours.