Paper: GS – II, Subject: Science and Technology, Topic: Nuclear Technology, Issue: India’s Nuclear Power.
Context:
India’s ambitious goal of achieving 100 GW of nuclear power generating capacity by 2047.
- It highlights the necessity of involving foreign partners and private entities in the nuclear sector, which has traditionally been government-controlled.
- The required changes in legislative, financial, and regulatory frameworks, including potential amendments to the Atomic Energy Act, 1962, and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (CLNDA), 2010.
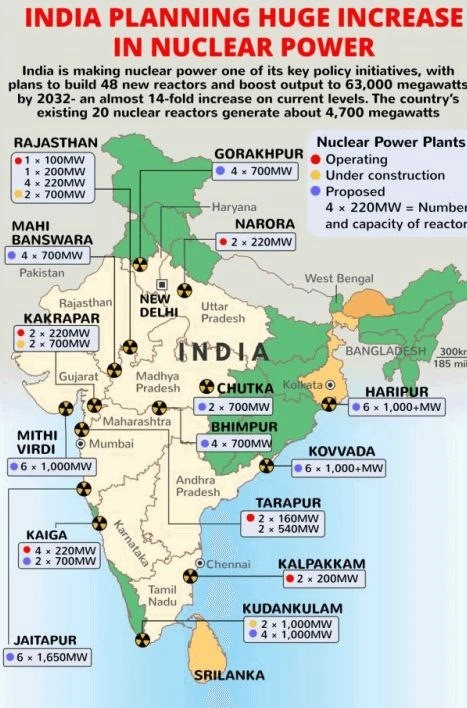
Key Takeaways:
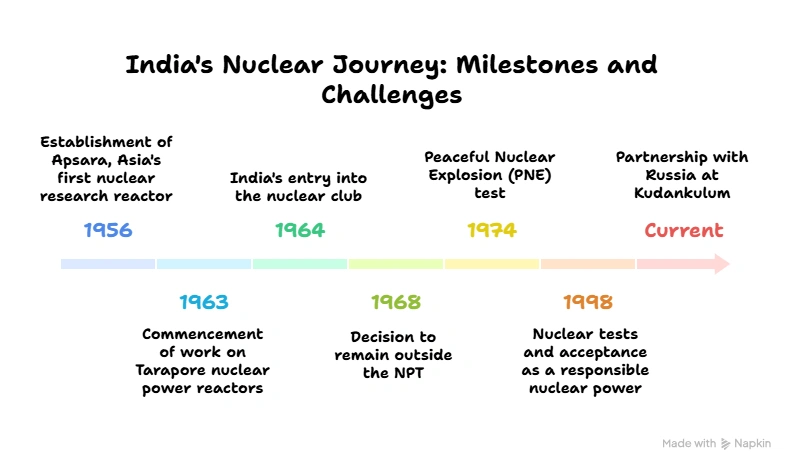
India’s Three-stage Nuclear Power Programme:
Stage 1: Natural Uranium Fuelled Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs):
- In the first stage, natural uranium was used as fuel for Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors, which also produced plutonium-239 as a byproduct while generating electricity.
- The second stage would also utilize the byproduct plutonium-293.
- The main reasons for selecting PHWRs for the First Stage of the Indian nuclear power programme in the 1960s were:
- The use of natural uranium oxide as the fuel.
- The best utilisation of mined uranium in energy production.
- The prospect of establishing a completely self-sufficient technology.
Stage 2: Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs): Utilizing Plutonium-Based Fuel:
- The second stage involves using plutonium-239 to produce mixed-oxide fuel, which would be used in Fast Breeder Reactors.
- Furthermore, thorium will be used in the reactor to create uranium-233 once there is a sufficient stockpile of plutonium-239. This uranium is essential for the third stage.
Stage 3: Advanced Nuclear Power Systems for Utilization of Thorium:
- The primary goal of stage 3 is to achieve a long-term nuclear fuel cycle.
- The advanced nuclear system would combine thorium and uranium-233.
- So, using a thermal breeder reactor, India’s abundant thorium would be utilized. This stage is currently in the research phase.
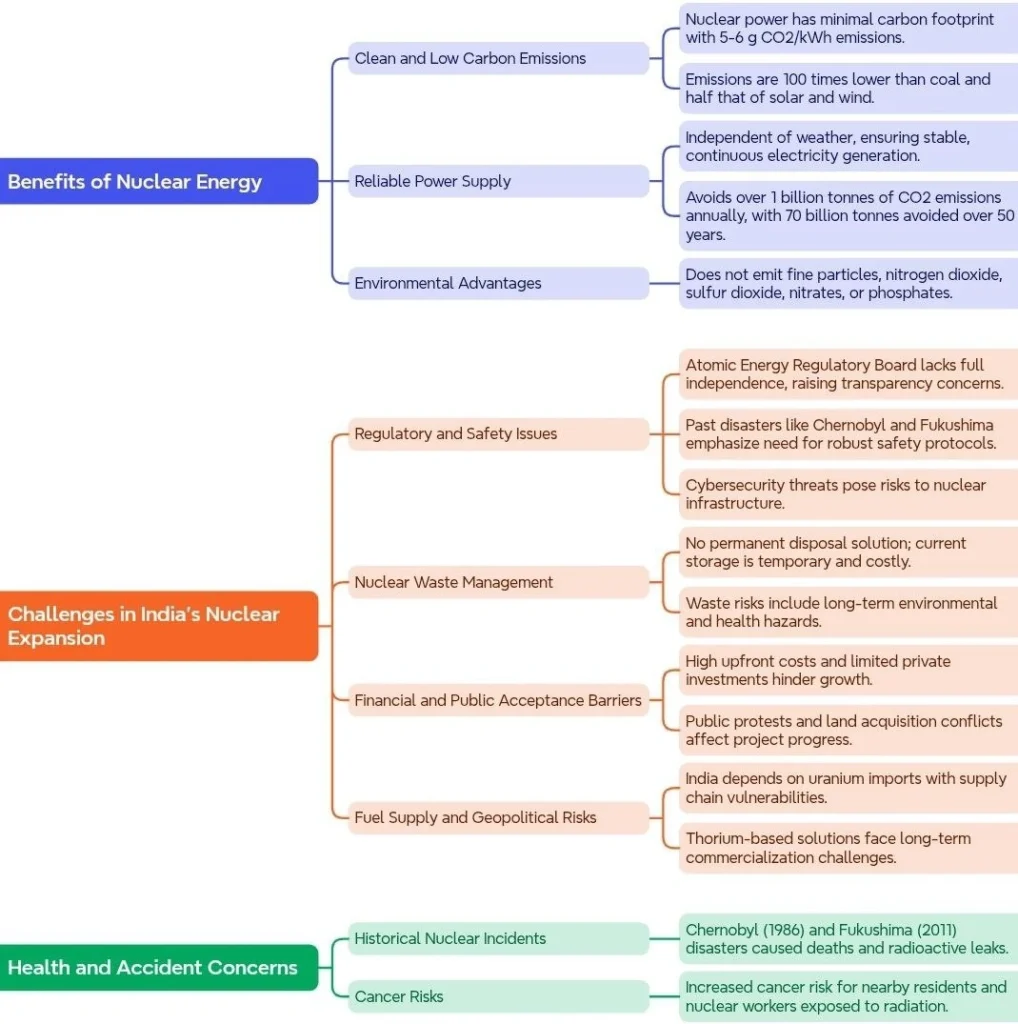
Benefits and Challenges of Nuclear Energy:
Conclusion:
For India to realize its ambitious goal of 100 GW of nuclear energy by 2047, a comprehensive approach is required. This includes legal reforms, encouraging private investments, enhancing regulatory frameworks, and improving public acceptance of nuclear energy. Only through decisive action can India effectively leverage nuclear power as a cornerstone of its energy strategy for sustainable development and economic growth.
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/redeeming-indias-nuclear-power-promise/article69842203.ece
La Excellence IAS Academy, the best IAS coaching in Hyderabad, known for delivering quality content and conceptual clarity for UPSC 2025 preparation.
FOLLOW US ON:
◉ YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPrepTeam
◉ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LaExcellenceIAS
◉ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/laexcellenceiasacademy/
GET IN TOUCH:
Contact us at info@laex.in, https://laex.in/contact-us/
or Call us @ +91 9052 29 2929, +91 9052 99 2929, +91 9154 24 2140
OUR BRANCHES:
Head Office: H No: 1-10-225A, Beside AEVA Fertility Center, Ashok Nagar Extension, VV Giri Nagar, Ashok Nagar, Hyderabad, 500020
Madhapur: Flat no: 301, survey no 58-60, Guttala begumpet Madhapur metro pillar: 1524, Rangareddy Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Bangalore: Plot No: 99, 2nd floor, 80 Feet Road, Beside Poorvika Mobiles, Chandra Layout, Attiguppe, Near Vijaya Nagara, Bengaluru, 560040
