Syllabus: GS-I, Subject: Geography, Topic: Resources – World and India, Issue: Multilateral treaties on rivers.
Context: Reports by ICIMOD and the Australian Water Partnership on water sharing treaties.
Highlights of the Report:
- Integrated river basin management is crucial for resilience to climate change in South Asia.
- Integrated river basin management refers to a basin-wide approach to river planning, backed by quality data sharing on water availability, biodiversity and pollution between all stakeholders.
- Underscores the necessity for multilateral treaties, particularly focusing on the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers.
Recommendations:
- Greater ‘hydro-solidarity‘ and climate diplomacy urged among countries.
- Emphasis on harnessing indigenous and local knowledge for crisis resolution.
- Plugging data gaps, enhancing water management, early warning systems, and disaster management.
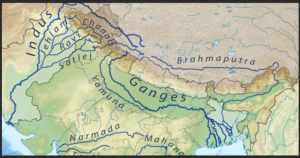
✔ Originates in the Tibetan Plateau.
✔ Flows through India Pakistan into the Arabian Sea.
✔ Governed by the Indus Water Treaty (1960) between India and Pakistan
Ganges:
✔ Originates in the Himalayas (Gangotri Glacier).
✔ Flows through India and Bangladesh.
✔ Initiatives like Namami Gange focus on its cleanup.
Brahmaputra:
✔ Originates in Tibet, flows through India’s northeastern states.
✔ Joins the Ganges in Bangladesh.
