CONTEXT:
Israel Chip Maker TOWER makes second bid to enter India with fabrication unit.
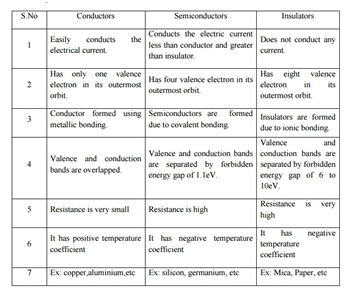
| WHAT ARE SEMI CONDUCTORS?Semiconductor, any of a class of crystalline solids intermediate in electrical conductivity between a conductor and an insulator. Ex: Antimony, Arsenic, Boron, Carbon, Germanium, Selenium, Silicon, Sulphur and Tellurium. |
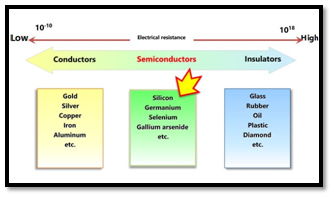
| Taiwan, accounts for 92% of the world’s most advanced semiconductor manufacturing capacity, while the Netherlands is the only country that produces chip-making machines and South Korea is one of the largest chip manufacturers. |
SEMI CONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING IN INDIA:

NEED FOR SEMI CONDUCTOR INDUSTRY:
Semiconductor chips serve as the fundamental building blocks and the “heart and brain” of modern electronics and information and communication technology (ICT) products.
- India is heavily dependent on imports for semiconductor and electronic products.
- Unlike other industries, where programmes like Production Linked Incentives bolster existing domestic industries, the semiconductor industry is being built almost entirely from scratch.
- Expected Consumption: In 2022, India’s consumption demand for semiconductors was marked at $24 billion and it is expected to touch $110 billion by 2023.
- India will consume semiconductors of around USD 70-80 billion to manufacture electronics products worth USD 300 billion by 2026.
- Export earnings → narrowing trade deficit
- Manufacturing and Export Target: India’s electronics vision document set a target of USD 300 billion in electronic manufacturing, with USD 120 billion in exports.
- Employment potential: To generate 6 lakh employment opportunities by 2030 in domains like fabrication, design, assembly and testing.
- Industry 4.0: Semiconductors and displays are at the core of modern electronics, driving the next phase of digital transformation under Industry 4.0.
GLOBAL SEMI CONDUCTOR MARKET:
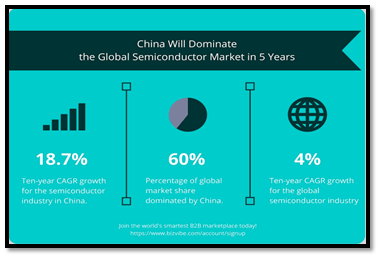
APPLICATION:

CAN INDIA BECOME A GLOBAL PLAYER IN SEMI CONDUCTOR INDUSTRY?
STRENGTHS
- The Indian talent pool: India has a large and growing pool of skilled engineers and scientists is a major asset for the Indian semiconductor industry, and it will be essential for the country’s success in the global market.
- The low costs: India’s low labor costs are another major advantage for the semiconductor industry. This makes India an attractive destination for foreign companies that are looking to set up chip manufacturing facilities.
- The government’s support: The Indian government has been a resolute supporter of the semiconductor industry.
The government has provided funding for research and development, tax breaks for domestic production, and other incentives to attract foreign investment. This support has been critical for the growth of the Indian semiconductor industry.
- India’s growing consumer electronics market can be a source of demand for semiconductor products, which can, in turn, fuel the growth of the industry.
CHALLENGES
- Development of this sector requires long-term support.
- Huge capital investment: Chip manufacturing is a cash-hungry business. Manufacturing of semiconductor chips require huge investments.
- High energy, electricity and water consumption is a concern for the environment and sustainability.
- Scarcity of semiconductor materials.
- Disposal problems- the fabrication process involves the use of toxic materials such as arsenic, antimony, and phosphorus, which can have adverse environmental effects.
- It requires highly skilled labor as the production of semiconductors as the fabrication process is intricate, involves 400- 1400 complex steps.
While India has the potential, it will take time and concerted efforts to become a global player in the semiconductor industry. Several countries with established semiconductor industries have a head start, but India can compete by leveraging its strengths and addressing the challenges. It would require a long-term commitment from both the public and private sectors.
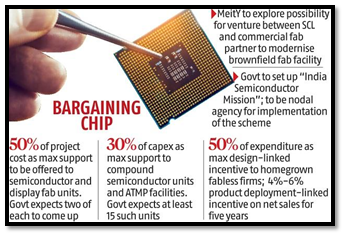
POLICY INITIATIVES IN INDIA:

- Production Linked Incentive Scheme:
In December 2021, the Indian government sanctioned Rs. 76,000 Cr under the PLI scheme to encourage the domestic manufacturing of various semiconductor goods.
- Make in India:
The ‘Make in India’ initiative, initiated in 2014, aims to boost manufacturing in India and establish the country as a global manufacturing hub.
- Semi-Conductor Mission:
India’s Semiconductor Mission was launched in 2021 for the development of sustainable semiconductors and display ecosystem in India.
- Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors (SPECS): For manufacturing of electronics components and semiconductors.
- Semicon India 2023 Conference:
It is an annual conference organized by the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) with the objective of promoting the growth and development of India’s semiconductor industry.

- Modified Electronics Manufacturing Clusters (EMC 2.0) Scheme:
The EMC 2.0 Scheme provides financial assistance for setting up of both EMC projects and Common Facility Centres (CFCs) across the country.
- Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL) Modernization:
The Government of India is actively pursuing modernization of the existing Semi-Conductor Laboratory (SCL) in Mohali as part of the broader efforts to grow semiconductor manufacturing in India.
STATE WISE INITIATIVES
- Rajasthan-based Sahasra Semiconductor, which is part of India’s Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors (SPECS), has stated that it will begin the commercial production of the first made-in-India memory chips at its Bhiwadi plant from September or early October 2023.
- The Vedanta group and the Foxconn of Taiwan have come together to build the first semiconductor manufacturing unit in Dholera of Gujarat. The companies signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the Gujarat Government.
INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENTS
- US President Joe Biden and Modi signed the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on Semiconductor Supply Chain and Innovation Partnership with the objective of coordinating semiconductor incentive programmes of India and the US.

WHAT INDIA CAN DO FURTHER?
- Self-Reliance: India’s semiconductor production should include the entire value chain from design to fabrication, packaging, and testing.
- Government fiscal support: Support should be provided on the other parts of the chip-making chain, such as design centres, testing facilities, and packaging.
- Improve Collaboration: A collaborative environment between industry and government is essential.
- Favourable Ecosystem should be provided for chip manufacturers.
- Central and state governments must cooperate on policy priorities and execution to achieve the goal of self-reliance in this Amrit Kaal.
CONCLUSION:
While India has the potential, it will take time and concerted efforts to become a global player in the semiconductor industry. Several countries with established semiconductor industries have a head start, but India can compete by leveraging its strengths and addressing the challenges. It would require a long-term commitment from both the public and private sectors. The semiconductor industry is heavily dependent on intellectual property (IP) and patents. India needs to strengthen its IP regime and encourage innovation.
