Syllabus: GS-III
Subject: Science & Technology
Topic: Space Technology
Issue: Astronomy Concepts
Synopsis:
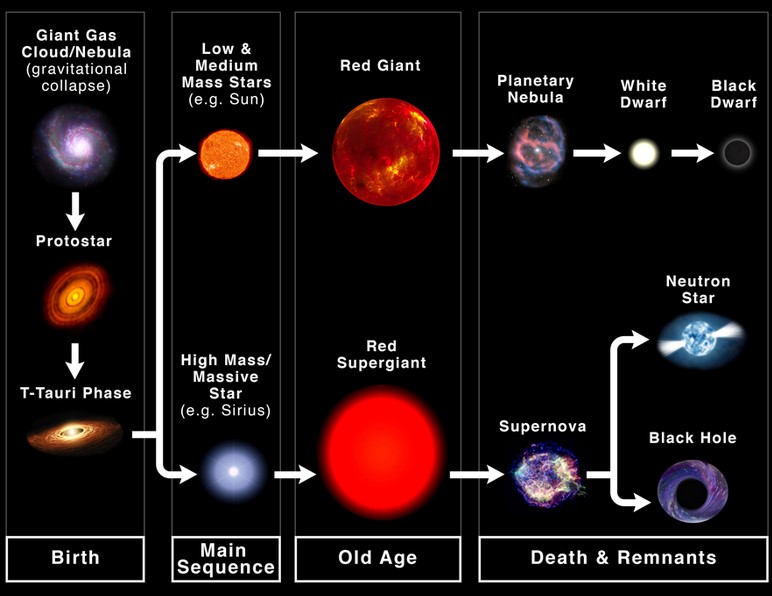
- The mass determines a star’s life cycle.
- Neutron Stars: When stars run out of fuel, their cores collapse under their own gravity.
- If the core is less dense, it becomes a neutron star, else it becomes a black hole.
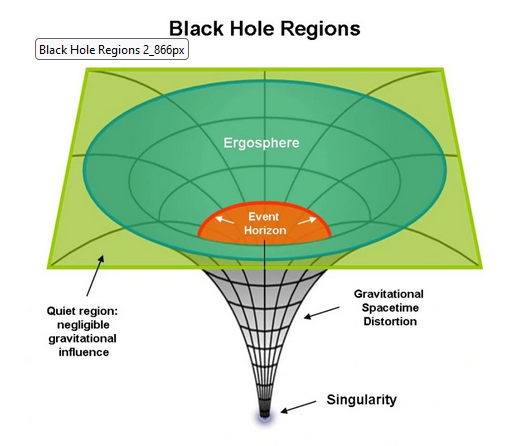
- Event Horizon:It is the point of no-return where the gravitational pull becomes so immense that not even light can escape.
-

- Singularity is the heart of the black hole, a point of infinite density where all the matter that fell in is concentrated.
- Chandrasekhar limit:Only stars whose mass is greater than 44 times of the sun turns into neutron stars/blackholes.
- Black Hole mass gap: Mass gap between heaviest possible neutron stars, (2.2 solar masses) and the lightest black holes(5 solar masses).

- Pulsars:Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars with strong magnetic fields that blast out pulses of radiation at regular intervals ranging from seconds to milliseconds.
- Millisecond Pulsars: Rotate significantly faster, with periods less than about 10 milliseconds.
- Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity : It suggests that instead of thinking of gravity as a force between masses, it is the bending or warping of space and time.
- Space and time are not separate entities but are interconnected called ad “spacetime”.
- Massive objects, like planets and stars, warp or curve the fabric of spacetime around them.
- Predicted the existence of gravitational waves – ripples in spacetime caused by the acceleration of massive objects.