| Syllabus: GS-II, Subject: International Relations, Topic: India’s foreign policy, Issue: Evolution of India’s foreign policy |
India’s foreign policy:
- India’s strategic geography has expanded to include island states and territories from the South Pacific to the African coast.
- The concept of the “Indo-Pacific” has gained prominence, driven by India’s evolving relations with China and the US.
- India’s engagement with Europe has increased, marked by high-level visits, growing trade, and agreements with the European Free Trade Association.
- The expansion of India’s geographic vocabulary has led to increased focus on regions like Europe, the Middle East, and Africa.
- Amid this expansion, “South Asia” has seen a decline, with SAARC’s failure prompting a shift towards sub-regional cooperation.
- New geographies like “Zomia” and “Khorasan” are gaining strategic attention due to emerging challenges and tensions in regions surrounding India.
| Prelims Connect (Places in news):
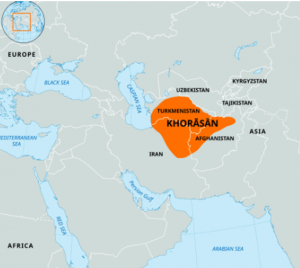
● Khorasan in Persian means the land of the rising sun. It refers to Persia’s eastern borderlands, including parts of modern Pakistan, Afghanistan and Central Asia.
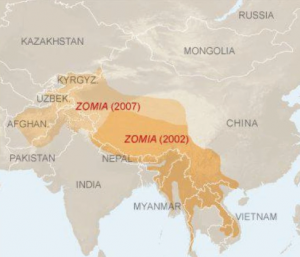
● Zomia– an academic term for a region where the highlands of North East India, South West China, and SouthEast Asia meet. ● It’s a region where centralized state control has been traditionally weak and is full of minority populations, some of whom straddle across formal state borders.
|